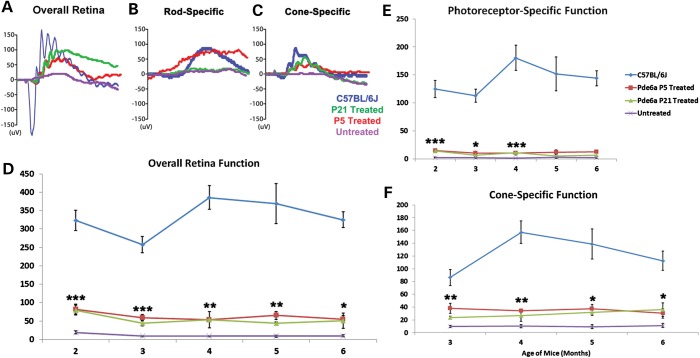
Figure 3.
Rescued visual function after AAV2/8(Y733F)-Rho-Pde6α transduction. Representative scotopic maximum ERG traces for a B6 control mouse (blue), a P5-treated eye (red), a P21-treated eye (green) and an untreated eye (purple) of a Pde6αD670G mouse at 5 months of age (A). Representative scotopic dim light rod-specific ERG traces of a B6 control mouse (blue), a P5-treated eye (red), a P21-treated eye (green) and an untreated eye (purple) of a Pde6αD670G mouse at 5 months of age (B), and representative photopic single flash cone-mediated ERG traces for a B6 control mouse (blue), a P5-treated eye (red), a P21-treated eye (green) and an untreated eye (purple) of a Pde6αD670G mouse at 5 months of age (C). Maximum scotopic b-wave amplitudes in a B6 mouse, the treated Pde6αD670G eyes and fellow-untreated eyes monthly between 2 and 6 months of age (D). Maximum scotopic photoreceptor-mediated a-wave amplitudes (shown as positive values) in a B6 mouse, the treated Pde6αD670G eyes and fellow-untreated eyes monthly between 2 and 6 months of age (E). Photopic cone-specific b-wave amplitudes in a B6 mouse, the treated Pde6αD670G eyes and fellow-untreated eyes from 3 to 6 months of age (F). Error bars show SEM for each time-point and the significance was calculated for the P21-treated eyes compared with untreated fellow eyes using the ratio paired t-test analysis. N ≥ 3 mice. *P < 0.05; **P < 0.01; ***P < 0.001.