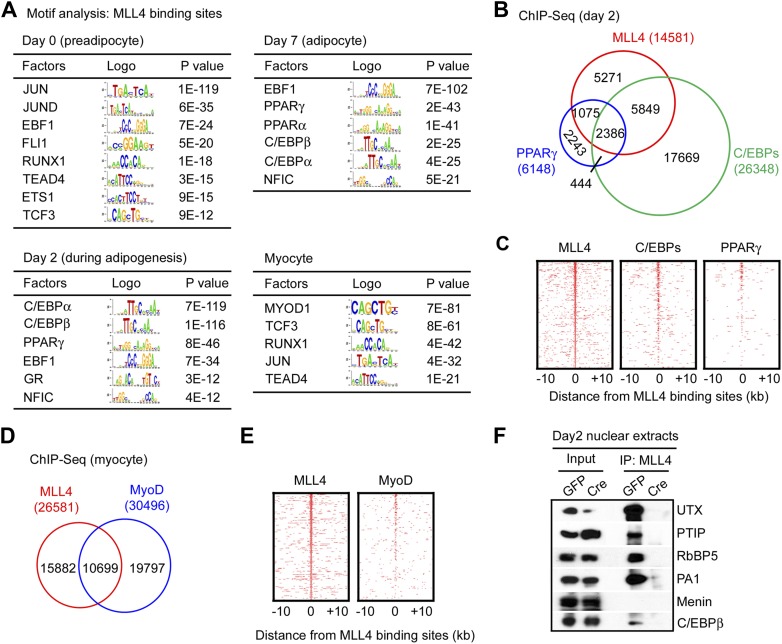
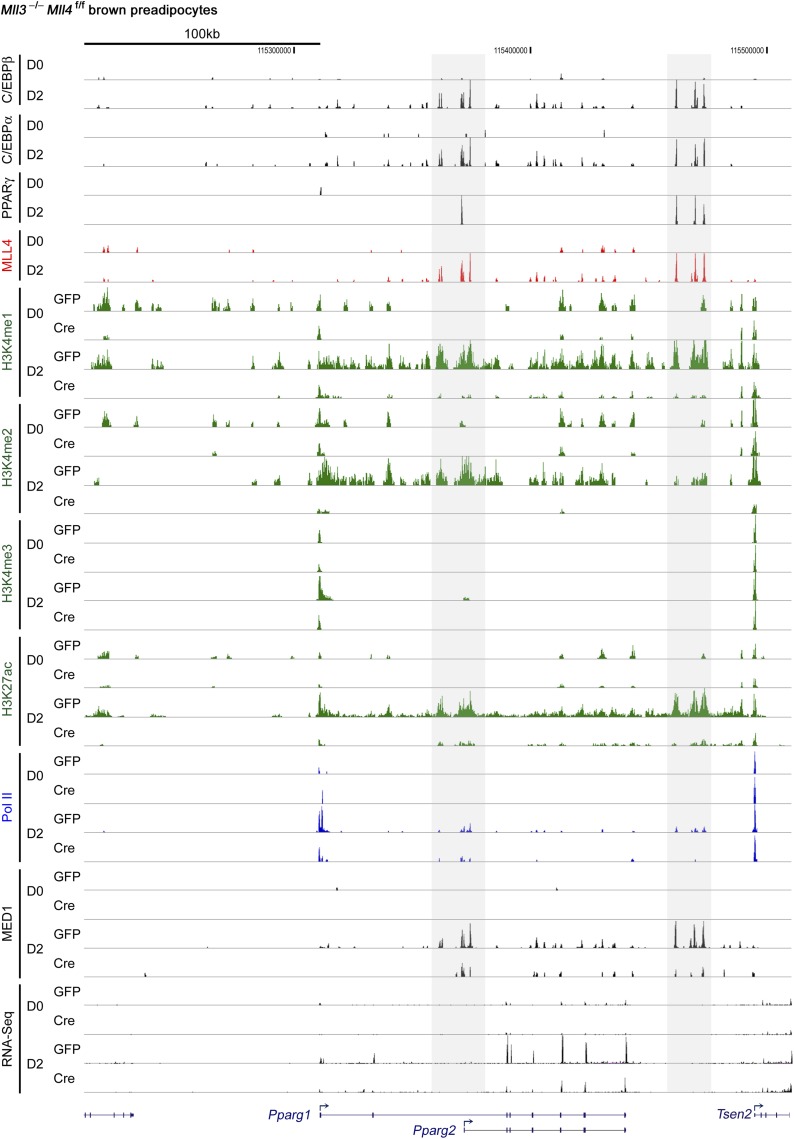
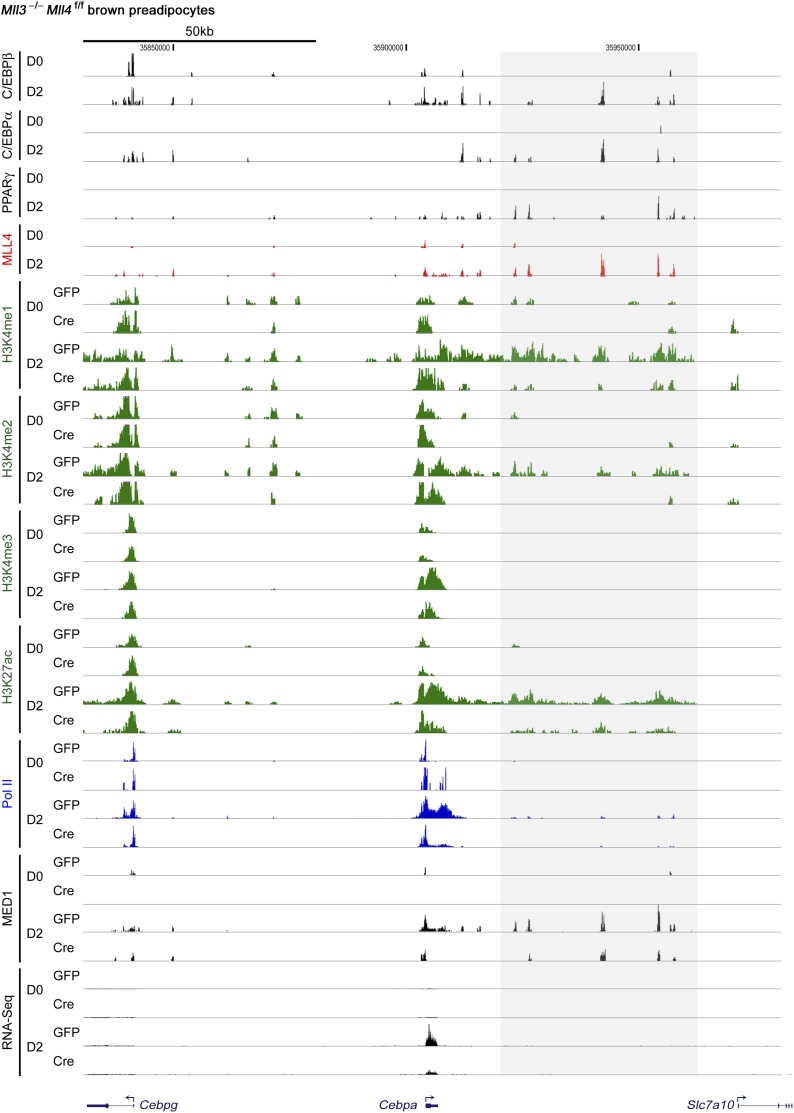
Figure 4. Genomic co-localization of MLL4 with lineage-determining TFs during differentiation.
(A) Adipogenic TF binding motifs are enriched at MLL4 binding regions during adipogenesis while myogenic TF binding motifs are enriched at MLL4 binding regions in myocytes. Top 2,000 emergent MLL4 binding regions at each time point were used for motif analysis. Only TFs that are expressed at the indicated cell type or differentiation stage are included. (B and C) Venn diagram (B) and heat maps (C) of genomic co-localization of MLL4 with C/EBPs (C/EBPα or β) and PPARγ at day 2 of adipogenesis. (D and E) Venn diagram (D) and heat maps (E) of genomic co-localization of MLL4 with MyoD in myocytes. (F) MLL4 physically interacts with C/EBPβ during adipogenesis. Nuclear extracts prepared at day 2 of adipogenesis were immunoprecipitated with MLL4 antibody. The immunoprecipitates were analyzed by Western blot using antibodies against MLL3/MLL4 complex components (UTX, PTIP, RbBP5 and PA1), Menin, or C/EBPβ.