Figure 17.13A.2.
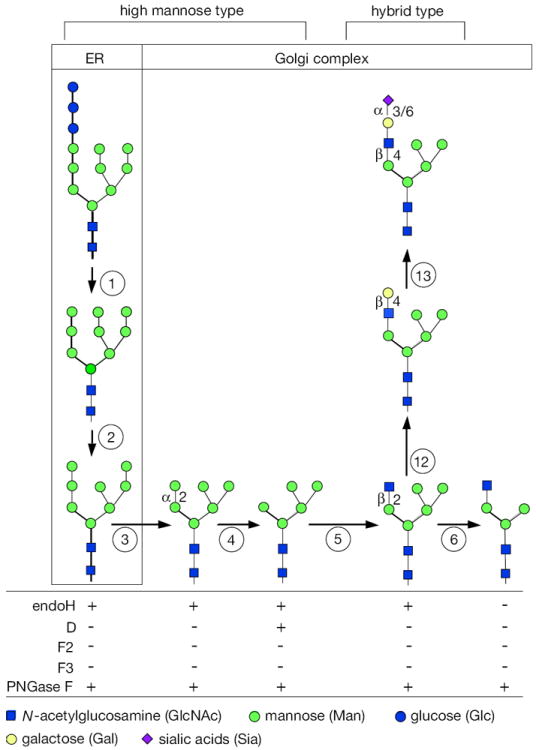
N-linked glycan maturation pathway for high-mannose and hybrid types, and sensitivities to various enzymes. Brackets (top) show the structures designated as high-mannose and hybrid chains. The boxes indicate ER or Golgi localization. The pathway begins with the precursor glycan (see Fig. 17.13A.1). Each successive numbered step in circles represents a glycosidase or glycosyl transferase that generates a new sugar chain with different sensitivities to the various endoglycosidases or PNGase F. (1) precursor glycan is trimmed by α-glucosidases I and II, removing three Glc. (2) ER mannosidase removes one Man. (3) α-Mannosidase I in Golgi complex removes two Man to make Man6GlcNAc2, with a single remaining α1-2Man. (4) The final α1-2Man is removed by a Golgi complex α-mannosidase I. (5) GlcNAc transferase I adds GlcNAc to Man5GlcNAc2. (6) α-Mannosidase II or α-mannosidase IIx (MX) removes the α1-3 and α1-6Man units to make GlcNAc1Man3GlcNAc2. Sensitivity to various enzymes (bottom) changes when moving from left to right, but remains the same within vertical columns. NOTE: This continued maturation to form complex chains is shown in Figure 17.13A.3. Additionally, these figures are not comprehensive; many glycosylation steps have not been included, but they do not affect the sensitivities to the enzymes listed. For the color version of the figure go to http://www.currentprotocols.com/protocol/mb1713a.
