Fig. 4.
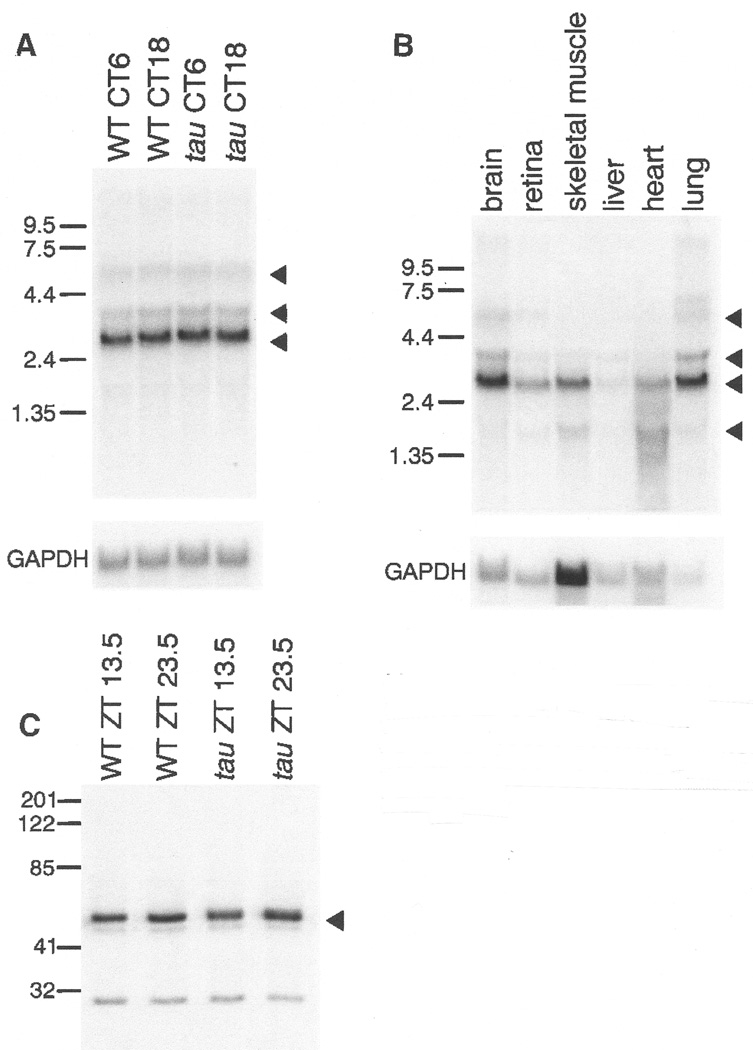
(A) Northern analysis (61) of total RNA prepared from brains of wild-type and homozygous tau hamsters collected at two circadian times, CT6 and CT18. A major transcript of 2.7 kb and minor transcripts of 3.5 and 5.9 kb are indicated by triangles. The blot was normalized by hybridization with probe to mouse GAPDH. (B) Northern analysis (61) of total RNA from wild-type hamster brain, retina, skeletal muscle, liver, heart, and lung tissue. A major transcript of 2.7 kb and minor transcripts of 1.6, 3.7, and 5.9 kb are indicated by triangles. The blot was normalized by hybridization with a probe to mouse GAPDH. (C) Immuno-blot of wild-type and tau hamster hypothalamic tissue extracts (61). Tissues were collected at two zeitgeber (ZT) times (13.5 and 23.5). Blots were probed with antibody to human CKIɛ. A strong signal is evident at ∼48 kD (triangle), the reported size of human CKIɛ (77).