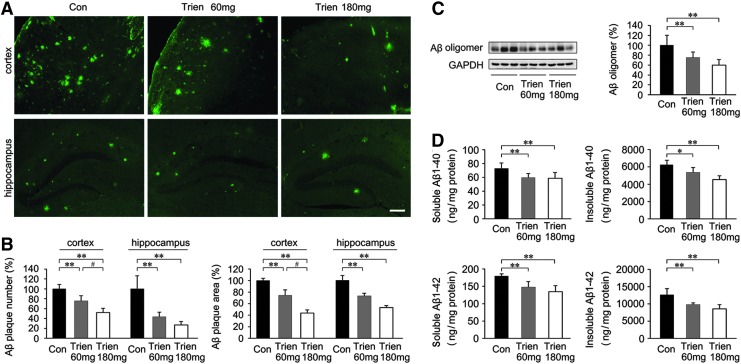
FIG. 3.
Effects of Trien administration on Aβ generation and Aβ plaque deposition in APP/PS1 mouse brain. (A) Fluorescent labeling of Aβ showing the Aβ plaques in the cortex and hippocampus of APP/PS1 mice brain in the vehicle control group and Trien-treated groups at doses of 60 mg/kg and 180 mg/kg, respectively. (B) Quantification of fluorescence indicated that Trien administration significantly reduced Aβ plaques number and area, both in the cortex and in the hippocampus. Scale bar=100 μm. (C) Western blot analysis showed that the protein levels of Aβ oligomer were markedly reduced in the Trien-treated mice brain compared with controls. GAPDH was used as an internal control. (D) Results of ELISA Aβ 1–40 and Aβ 1–42 assays showed that Trien treatment led to a decrease in Aβ production. The level of Aβ was standardized to cortex tissue protein and expressed as Aβ ng/mg of tissue protein. All values are mean±SEM (n=6). *p<0.05, **p<0.01 versus the control group, #p<0.05 versus Trien 60 mg/kg treatment group (one-way ANOVA post hoc Fisher's PLSD).