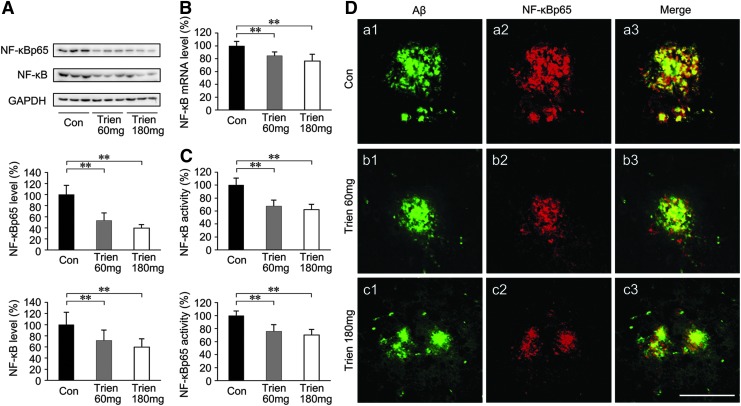
FIG. 7.
Effects on NF-κB in the APP/PS1 mouse brain under Trien treatment conditions. The expression and activity of NF-κB in the APP/PS1 mouse brain is shown for both Trien-treated groups and the vehicle-treated control group. (A) Western blot analysis showed that Trien administration significantly downregulated NF-κB. Protein levels of total NF-κB and NF-κBp65 subunit were markedly reduced in the brain-derived nuclear extracts from the Trien-treated APP/PS1 mice. (B) Real-time PCR assays indicated that the mRNA level of NF-κB in the brain-derived nuclear extracts of the Trien-treated group was significantly reduced. (C) Trien treatment induced an inhibition of nuclear activation of total NF-κB, and NF-κBp65, in brain-derived nuclear extracts of APP/PS1 mouse. (D) Double immunofluorescence labeling by anti-Aβ (a1, a2, a3) and anti-NF-κBp65 (b1, b2, b3) showed the colocalization of NF-κB immunoreactivity Aβ-positive plaques (c1, c2, c3). Scale bar=50 μm. All values are mean±SEM (n=6). **p<0.01 versus the control group (one-way ANOVA post hoc Fisher's PLSD).