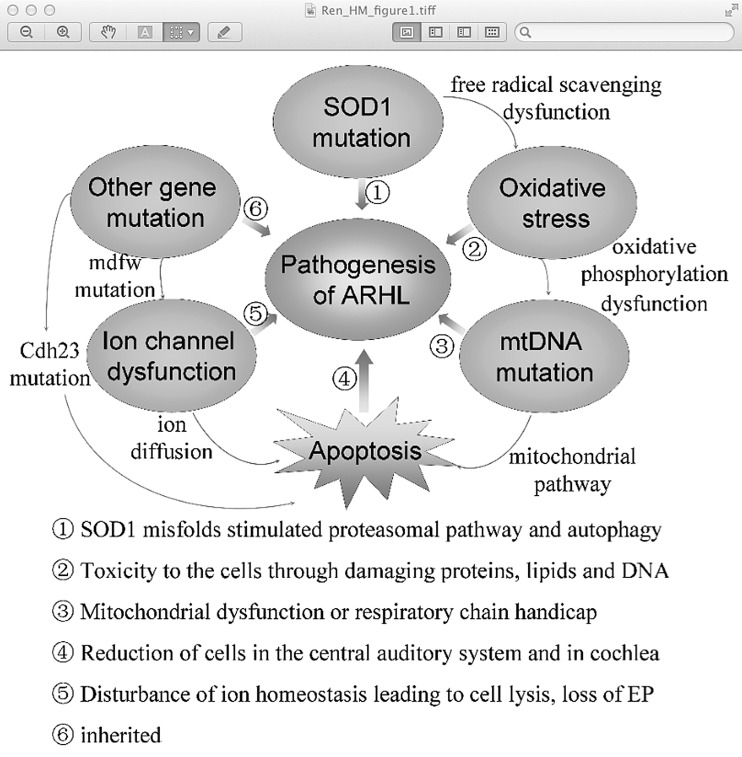
FIG. 1.
The mechanism of age-related hearing loss (ARHL). The SOD1 mutation, as an initial event accelerating ARHL through stimulating the proteasomal pathway and autophagy, directly leads to free radical scavenging dysfunction, which in turn stimulates mitochondrial (mt) DNA mutation. mtDNA mutations are not only toxic to the auditory cells by damaging proteins, lipids, and DNA in cells but also results in cell apoptosis through the mitochondrial pathway, which untimately leads to ARHL. Other gene mutations such as the Cdh23 mutation may be harmful to the stereociliary tip link and cause hair cell apoptosis from the base to apex, leading to early onset of ARHL. Meanwhile, the mdfw mutation leads to the plasma membrane Ca2+ ATPase2 dysfunction, finally resulting in cell apoptosis and even the appearance of ARHL.