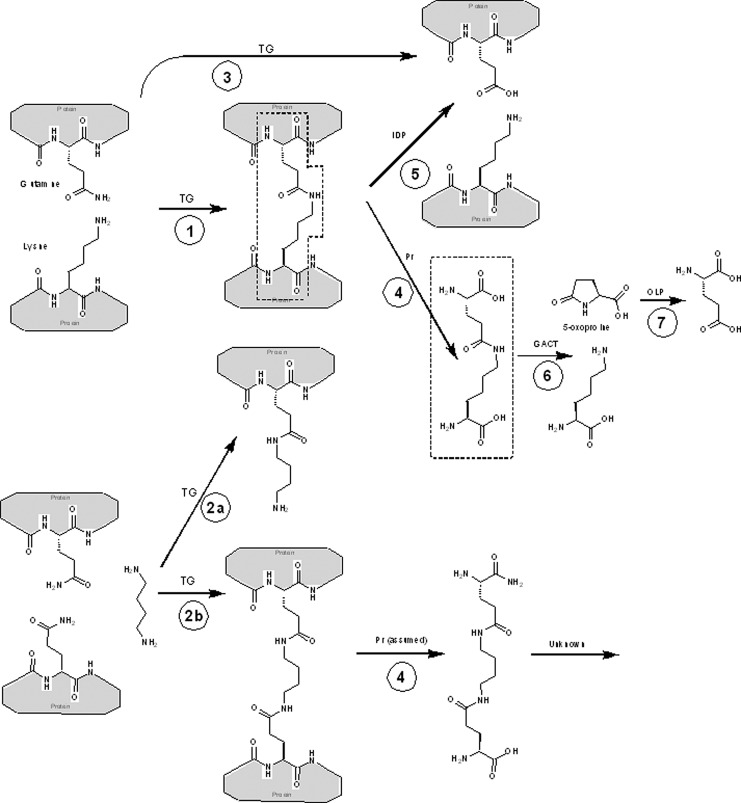
FIG. 1.
Transglutaminase cross-links. Key chemical structures discussed in this review and their interconversion. ε-(γ-glutamyl)-lysine (EGGL) moieties are outlined in dotted lines. Key: Gray boxes represent proteins, whose sequence contains the indicated amino acids. Specific catalyzed reactions are: (1) cross-linking of two proteins with transglutaminase (TG); (2a) linking of a protein with an amine (here putrescine used as an example) with TG, and (2b) cross-linking of two proteins via an amine; (3) hydrolysis of glutamine to glutamate, catalyzed by TG; (4) proteolysis of proteins with any protease (PR) releases free cross-link; (5) isodipeptidase (IDP) cleavage of cross-link regenerates original, unlinked proteins; (6) γ-glutamylamine cyclotransferase (GACT) cleaves isolated EGGL to lysine and 5-oxoproline; (7) 5-oxo-l-prolinase (OLP) cleaves 5-oxoproline to form l-glutamate.