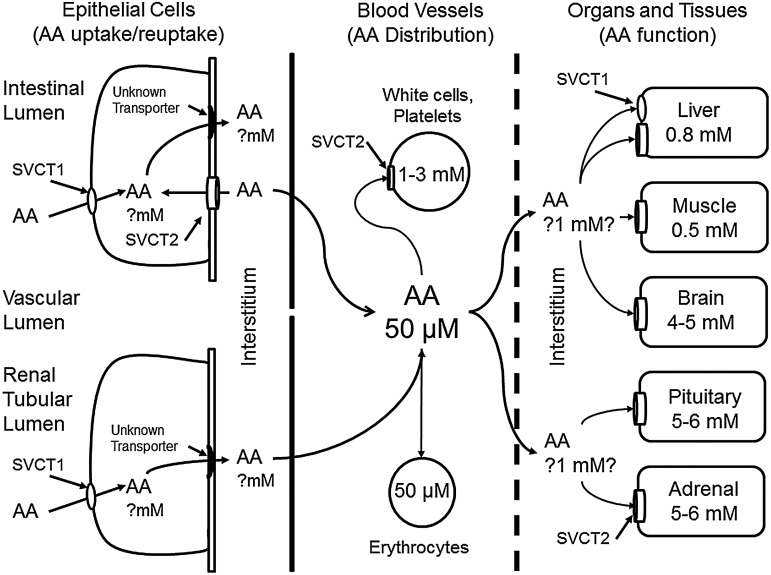
FIG. 2.
Uptake and distribution of ascorbate across the vascular bed. Ascorbate (AA) is taken up from the intestine either on the SVCT1 or as DHA on glucose transporters (not shown). Once inside the intestinal epithelium, it exits by an unknown mechanism on the basolateral membrane into the interstitium and then into nearby capillaries. Ascorbate in the bloodstream is taken up by erythrocytes (either as DHA or as slow diffusion) and by leukocytes and endothelial cells on the SVCT2. Plasma ascorbate is distributed by the vascular tree to organ beds. Interstitial ascorbate is then taken up by the SVCT2 on nucleated cells in the organs. In the central nervous system, ascorbate enters the cerebrospinal fluid largely by secretion from the choroid plexus (not shown). SVCT1, sodium-dependent vitamin C transporter 1; SVCT2, sodium-dependent vitamin C transporter 2.