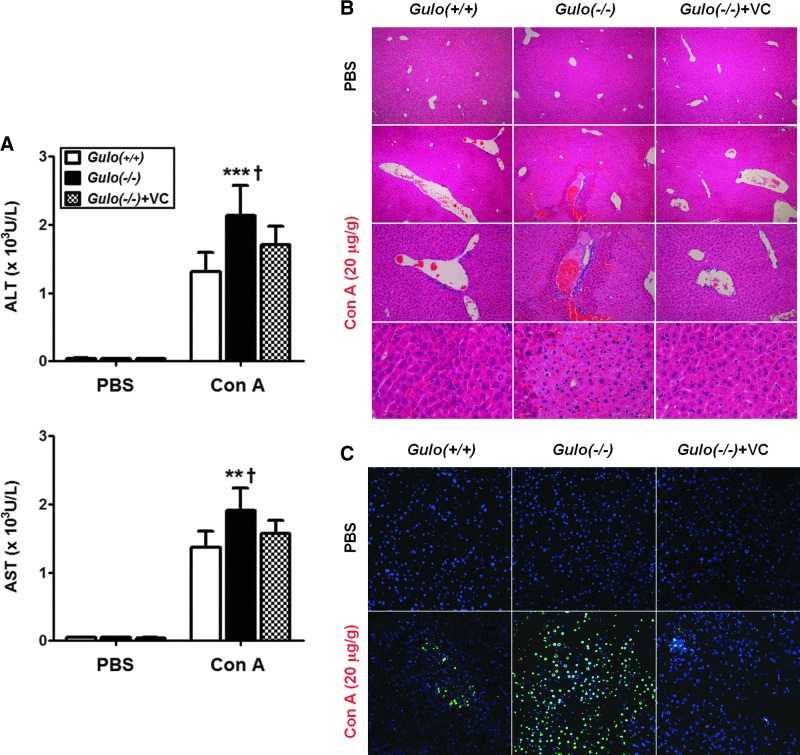
FIG. 1.
The extensive liver damage in vitamin C-insufficient Gulo(−/−) mice in response to Con A. WT [Gulo(+/+)], vitamin C-insufficient [Gulo(−/−)], and vitamin C-sufficient [Gulo(−/−)+VC] mice were intravenously injected with 20 μg/g of Con A or PBS. Mice were sacrificed at 18 h after injection. (A) The increase of the plasma ALT and AST levels by Con A injection [n=8–9, **p<0.01 or ***p<0.001 vs. Gulo(+/+), †p<0.05 vs. Gulo(−/−)+VC]. Liver injury was quantified by measuring the plasma levels of ALT and AST using a kit according to the manufacturer's instructions. (B) The extensive liver injury by Con A injection. Liver tissues were harvested, fixed, sectioned, and stained with hematoxylin and eosin as described in the Materials and Methods section. The lesions were examined surrounding the hepatic veins, and the results are the representative of more than three experiments (n=9). (C) The extensive apoptosis in the liver by Con A injection. Apoptotic cells in the liver were also detected by the TUNEL method as described in the Materials and Methods section. The nuclei were counterstained with DAPI, and the results are the representative of more than three experiments (n=9). ALT, alanine transaminase; AST, aspartate transaminase; Con A, concanavalin A; Gulo, l-gulonolactone-γ-oxidase; TUNEL, terminal deoxynucleotidyl transferase dUTP nick-end labeling; Vitamin C, l-ascorbic acid; WT, wild-type. To see this illustration in color, the reader is referred to the web version of this article at www.liebertpub.com/ars