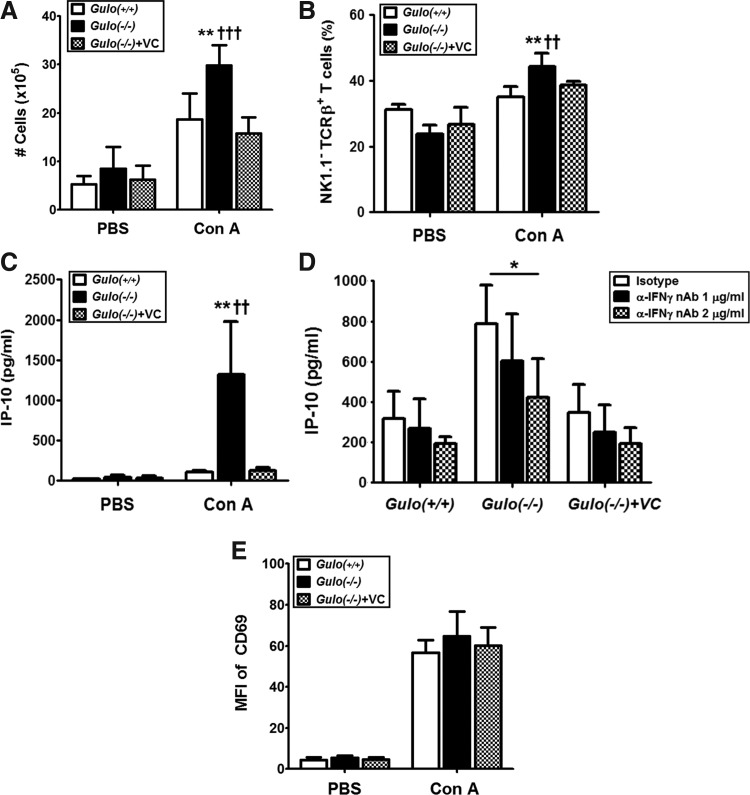
FIG. 3.
Increasing numbers of liver-infiltrating T-cells in vitamin C-insufficient Gulo(−/−) mice in response to Con A. After WT [Gulo(+/+)], vitamin C-insufficient [Gulo(−/−)], and vitamin C-sufficient [Gulo(−/−)+VC] mice were intravenously injected with 20 μg/g of Con A or phosphate buffered saline (PBS), liver MNCs were isolated at different time points. (A) Increase of the total number of liver MNCs 6 h after Con A injection [n=6, **p<0.01 vs. Gulo(+/+), †††p<0.001 vs. Gulo(−/−)+VC]. (B) Increase of the T-cell frequency in liver MNCs by Con A injection. Six hours after injection, the frequency of T-cells (NK1.1− TCRβ+) in liver MNCs upon Con A injection was analyzed by flow cytometry analysis as described in the Materials and Methods section [n=5, **p<0.01 vs. Gulo(+/+), ††p<0.01 vs. Gulo(−/−)+VC]. (C) Increased IP-10 production from liver MNCs by Con A injection. Four hours after injection, liver MNCs were isolated and cultured for 24 h as described in the Materials and Methods section. The amounts of IP-10 in the supernatants were determined by ELISA [n=10, **p<0.01 vs. Gulo(+/+), ††p<0.01 vs. Gulo(−/−)+VC]. (D) Suppression of IP-10 production by the neutralization of IFN-γ bioactivity. Four hours after injection, liver MNCs were isolated and cultured with anti-mouse IFN-γ (1 and 2 μg/ml) or isotype antibody (2 μg/ml). The amounts of IP-10 in the supernatants were determined by ELISA (n=5, *p<0.05). (E) The equal activation status of liver MNCs. Four hours after injection, liver MNCs were isolated, and surface expression of CD69 was measured by flow cytometry. The mean fluorescence intensity (MFI) of CD69 is represented as the mean±SD (n=5). IP-10, IFN-inducible protein-10.