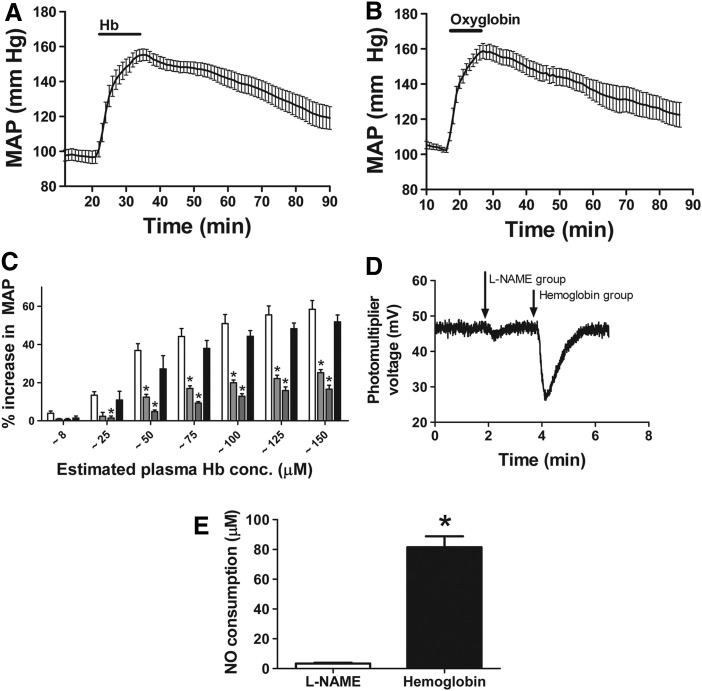
FIG. 1.
Effect of hemoglobin and Oxyglobin infusion on mean arterial pressure (MAP). (A) Average change in MAP over time after infusion of 175 mg/kg purified human hemoglobin (Mean±SEM, n=6). (B) Average change in MAP over time after infusion of 175 mg/kg Oxyglobin (Mean±SEM, n=5). (C) Percentage increase in MAP after infusion of 175 mg/kg hemoglobin analogs. Plasma concentration was estimated to be ∼8, 25, 50, 75, 100, 125, and 150 μM. Human hemoglobin (▭), methemoglobin ( ), cyano-methemoglobin (
), cyano-methemoglobin ( ), and Oxyglobin (
), and Oxyglobin ( ). (Mean±SEM, n=5). *Significantly different (p<0.05) from hemoglobin by two-way ANOVA with Bonferroni correction. (D) Raw data for plasma NO consumption after experiment as analyzed by triiodide chemiluminescence. L-NAME infusion and hemoglobin infusion were compared. (E) Plasma NO consumption determined at the end of experiments in which either L-NAME or hemoglobin was infused. Mean±SEM (n=5). *Significantly different (p<0.0001) from L-NAME group. L-NAME, L-NG-Nitroarginine methyl ester; NO, nitric oxide.
). (Mean±SEM, n=5). *Significantly different (p<0.05) from hemoglobin by two-way ANOVA with Bonferroni correction. (D) Raw data for plasma NO consumption after experiment as analyzed by triiodide chemiluminescence. L-NAME infusion and hemoglobin infusion were compared. (E) Plasma NO consumption determined at the end of experiments in which either L-NAME or hemoglobin was infused. Mean±SEM (n=5). *Significantly different (p<0.0001) from L-NAME group. L-NAME, L-NG-Nitroarginine methyl ester; NO, nitric oxide.