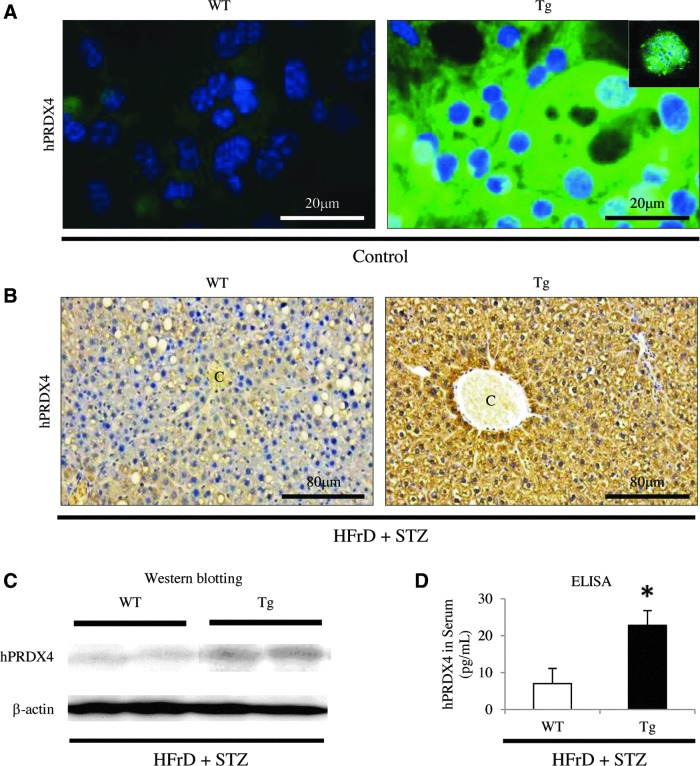
FIG. 2.
Analysis of the expression of hPRDX4 protein in the mice. (A) Immunofluorescence staining showed that, in vitro, hPRDX4 was specifically expressed in hepatocytes harvested from Tg mice, but not in those from WT mice, under basal conditions (control, n=5 mice per group). The hPRDX4 protein and ER-Tracker Blue-White were intracellularly colocalized in hepatocytes obtained from Tg mice (inset). Scale bar=20 μm. (B) At 8 weeks after HFrD feeding and STZ injection (HFrD+STZ, n=10 mice per group), hPRDX4 was detected in many hepatocytes throughout the liver of Tg mice, and was weakly detected in a very small number of hepatocytes from WT mice, indicating weak cross-reactivity between hPRDX4 and endogenous mPRDX4. C, central vein. Scale bar=80 μm. (C) Western blotting showed increased hepatic hPRDX4 protein expression in HFrD+STZ Tg mice (n=10 mice per group). Very faint bands were detected in WT mice, indicating weak cross-reactivity of the antibody for mPRDX4, as shown in Figure 2B. (D) ELISAs confirmed that serum hPRDX4 levels were elevated in HFrD+STZ Tg mice (n=10 mice per group), revealing that only Tg mice had markedly elevated hPRDX4 levels, but not in WT mice (*p<0.05). Values are means±SE and were normalized for β-actin expression (western blotting). ELISA, enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay; ER, endoplasmic reticulum. To see this illustration in color, the reader is referred to the web version of this article at www.liebertpub.com/ars