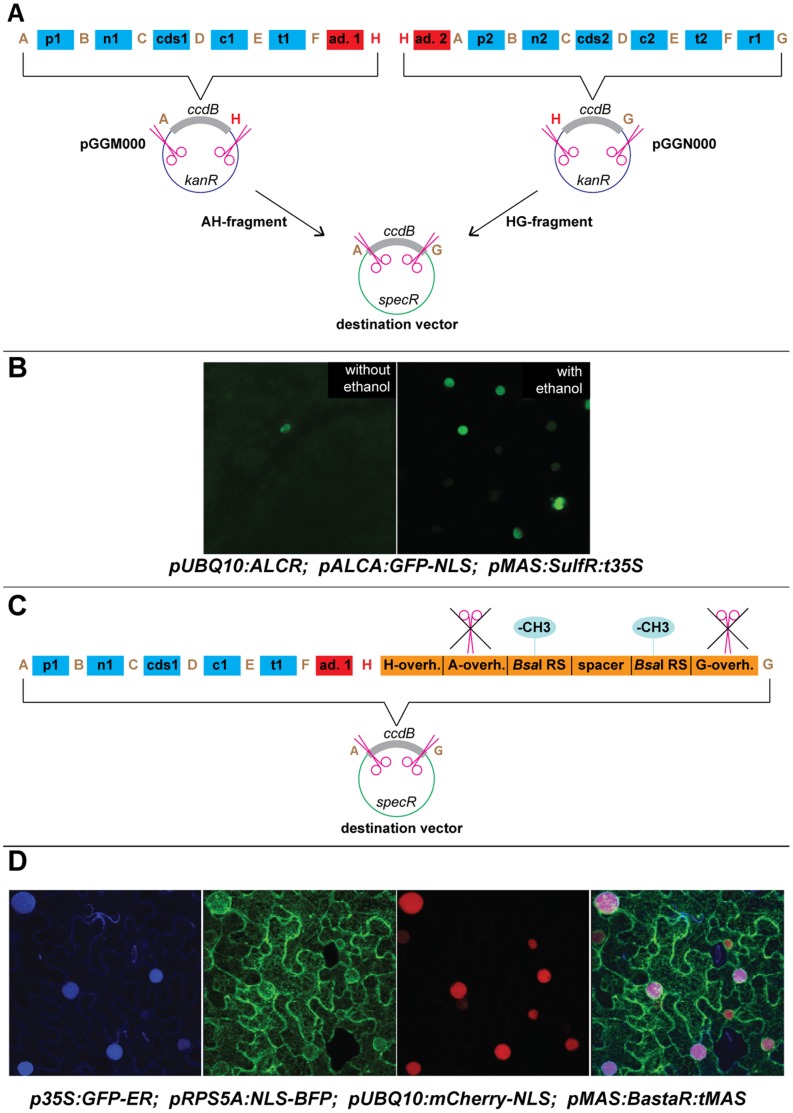
Figure 4. Multiple expression cassettes on a single T-DNA.
A) The first strategy uses one additional overhang (“H” = TAGG), two adapter modules and two intermediate vectors. In a first step, two expression cassettes (“supermodules”) are assembled in parallel in two different intermediate vectors (pGGM000 and pGGN000). The BsaI sites in the intermediate vectors are retained in the supermodule. In the second step, these two supermodules are then transferred into a destination vector via a normal GreenGate reaction. The overhang types are given in capital letters. p1/2 = promoter, n1/2 = N-terminal tag, cds1/2 = coding sequence, c1/2 = C-terminal tag, t1/2 = terminator, r1 = plant resistance, ad.1 = FH-adapter module, ad.2 = HA-adapter module. B) Fluorescence microscopy images show Nicotiana benthamiana leaves infiltrated with a construct harboring two expression cassettes on one T-DNA created via this method. The images were taken 72 hours after infiltration and 24 hours after ethanol induction (picture on the right). The first transcriptional unit drives constitutive expression of the ALCR transcription factor (pUBQ10:B-dummy-ALCR-D-dummy:tRBCS; pMAS:sulfR:t35S), the second one (pALCA:Ω-element-GFP-NLS-D-dummy:tRBCS) of nuclear localized GFP in presence of ethanol-bound ALCR protein. C) Only one additional element is required for the second strategy. Instead of a plant resistance cassette module, the FH-adapter module from strategy #1 and an oligo duplex (orange) with unpaired H and G overhangs are used in the GreenGate reaction. The oligo duplex contains internal BsaI sites that would result in A and G overhangs after digestion. However, digestion is blocked by methylation of the cytosine residues in the BsaI recognition sites, since BsaI is sensitive to methylation. After transformation of the resulting construct into bacteria, the methylation is lost during replication because no dcm site is present. Thus, after re-isolation from bacteria, the plasmid, already containing one expression cassette, can function as an empty GreenGate destination vector, releasing A and G overhangs after digestion by BsaI and removal of the BsaI recognition sites from the vector backbone. This process can in principle be re-iterated infinitely. The construct is finalized by using a standard plant resistance module in the last step. D) N. benthamiana leaves infiltrated with a destination vector (pTL019) carrying three transcriptional units assembled by this method. The fluorescence signal from all three individual expression cassettes, i.e. nuclear localized BFP (left), ER-localized GFP (second from left) and nuclear localized mCherry (third from left), is visible in all transformed cells. Merge shown on the right.