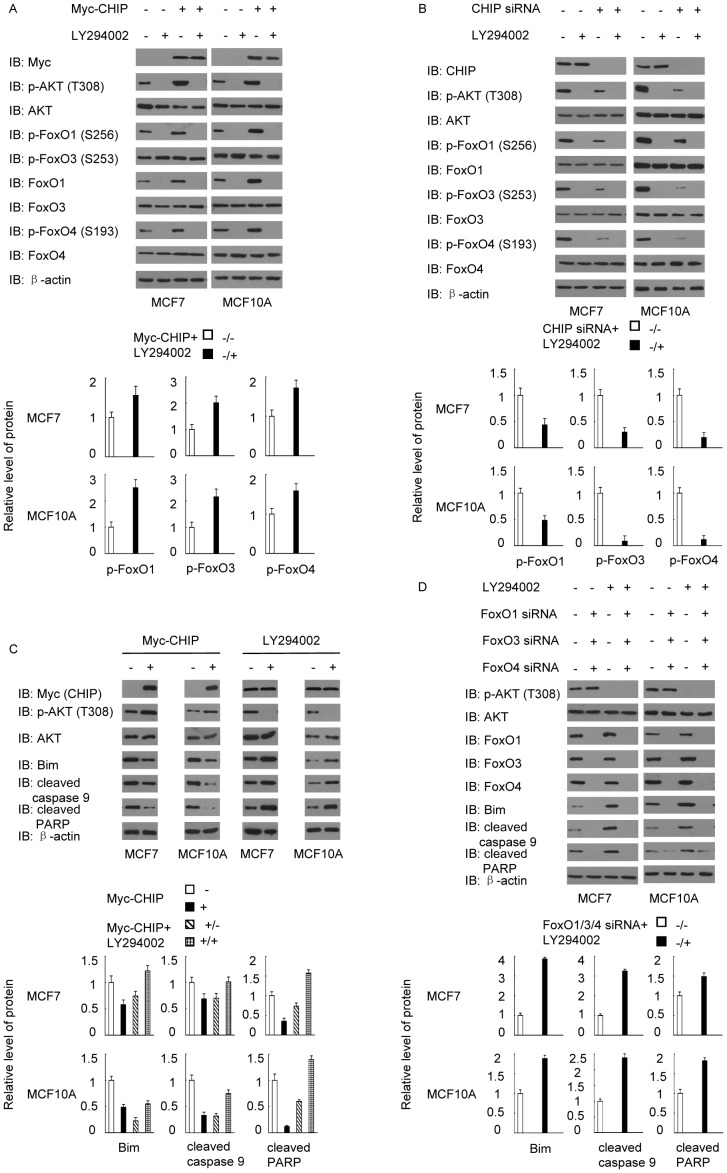
Figure 2. CHIP-induced AKT activation directly inhibited FoxO proteins, an occurrence closely correlated with apoptosis resistance.
(A) MCF7 and MCF10A cells were transfected with Myc-CHIP or Myc empty vectors as negative control. AKT inhibition with LY294002 (20 µmol/L, 1h) led to the activation of FoxO proteins. (B) Cells transfected with CHIP siRNA or negative control siRNA were treated with LY294002 (20 µmol/L, 1h) and immunoblotted for p-AKT (T308), p-FoxO1 (S256), p-FoxO3 (S253), and p-FoxO4 (S193). (C) AKT activation induced by CHIP overexpression led to the decrease in Bim, cleaved caspase 9, and cleaved PARP. Treatment with LY294002 (20 µmol/L, 1h) could reverse this effect. (D) Knockdown of FoxO1, FoxO3, and FoxO4 led to the decrease in Bim, cleaved caspase 9, and cleaved PARP. Treatment with LY294002 (20 µmol/L, 1h) could not reverse this effect.