Abstract
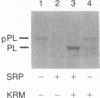
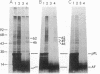
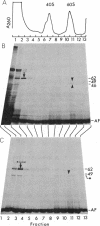
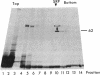
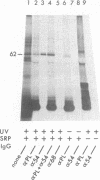
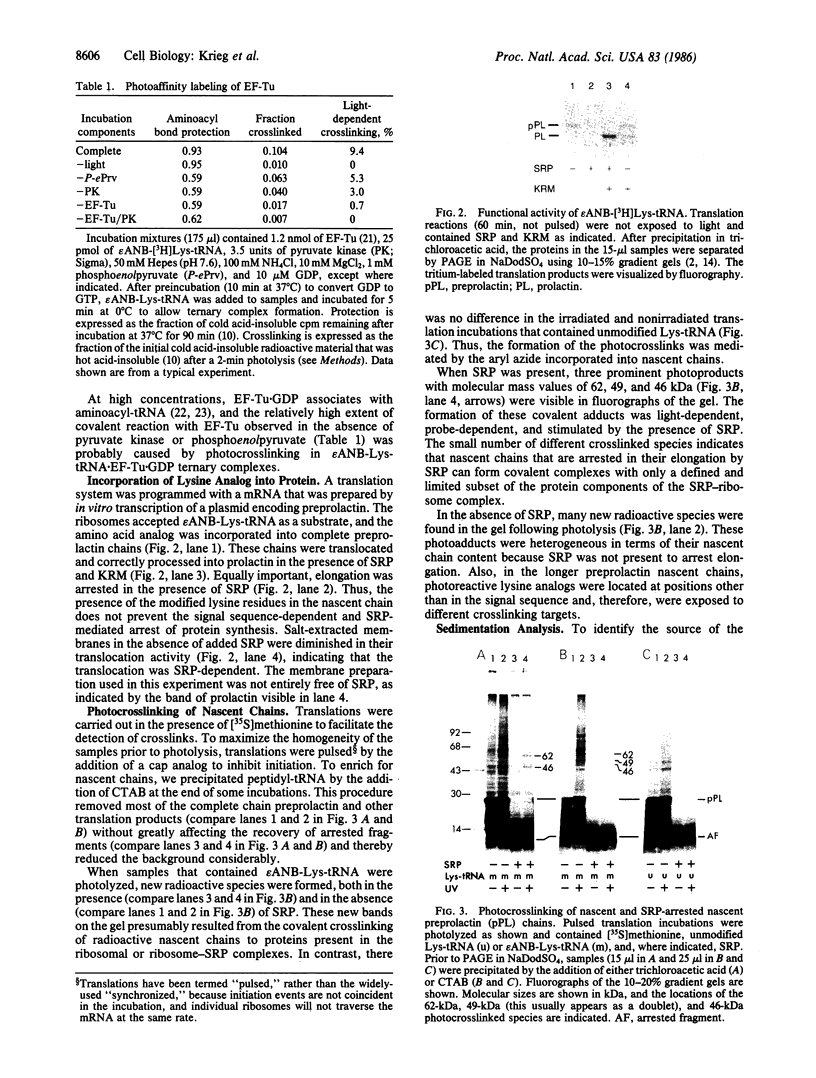
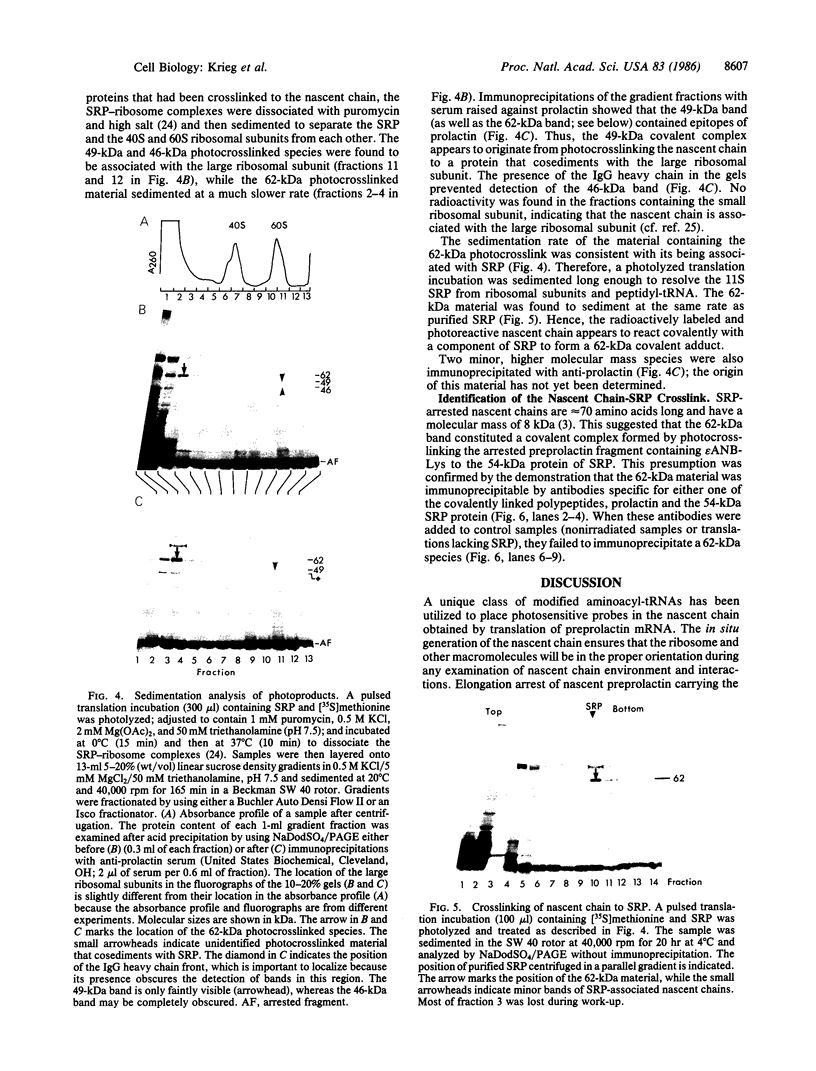
Photoreactive moieties were incorporated into nascent polypeptides in a wheat germ protein-synthesizing system by using a plasmid-derived preprolactin mRNA and a Lys-tRNA analog, N epsilon-(5-azido-2-nitrobenzoyl)-Lys-tRNA (epsilon ANB-Lys-tRNA). The presence of the abnormally large amino acid side chains in the nascent chains did not impair function: complete preprolactin chains were synthesized in the absence of the signal recognition particle (SRP), elongation was arrested in the presence of SRP, and SRP-dependent translocation across the membrane of the endoplasmic reticulum and signal peptidase cleavage were observed in the presence of salt-extracted microsomes. Photolysis of elongation-arrested ribosomes resulted in several light- and epsilon ANB-Lys-tRNA-dependent crosslinks. By using antibodies specific for each of the proteins, one covalent complex was shown to be a photocrosslink between the preprolactin nascent chain and the 54-kDa protein subunit of SRP. This demonstrates that the N-terminal end of a secretory protein is located adjacent to the SRP in elongation-arrested ribosomes and strongly suggests that the signal sequence is recognized by and binds to the 54-kDa subunit of SRP. The other photocrosslinks involve as-yet-unidentified proteins in the large ribosomal subunit, indicating that this method of incorporating probes provides a powerful approach to examining the environment and interactions of the nascent chain during translation and translocation across the membrane of the endoplasmic reticulum. The Lys-tRNA analog also successfully photoaffinity-labeled the Escherichia coli elongation factor Tu (EF-Tu) in the epsilon ANB-Lys-tRNA.EF-Tu.GTP ternary complex.
Full text
PDF


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bernabeu C., Lake J. A. Nascent polypeptide chains emerge from the exit domain of the large ribosomal subunit: immune mapping of the nascent chain. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1982 May;79(10):3111–3115. doi: 10.1073/pnas.79.10.3111. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Blobel G., Sabatini D. Dissociation of mammalian polyribosomes into subunits by puromycin. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1971 Feb;68(2):390–394. doi: 10.1073/pnas.68.2.390. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Erickson A. H., Blobel G. Cell-free translation of messenger RNA in a wheat germ system. Methods Enzymol. 1983;96:38–50. doi: 10.1016/s0076-6879(83)96007-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gilmore R., Blobel G. Transient involvement of signal recognition particle and its receptor in the microsomal membrane prior to protein translocation. Cell. 1983 Dec;35(3 Pt 2):677–685. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(83)90100-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gilmore R., Blobel G. Translocation of secretory proteins across the microsomal membrane occurs through an environment accessible to aqueous perturbants. Cell. 1985 Sep;42(2):497–505. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(85)90107-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gilmore R., Walter P., Blobel G. Protein translocation across the endoplasmic reticulum. II. Isolation and characterization of the signal recognition particle receptor. J Cell Biol. 1982 Nov;95(2 Pt 1):470–477. doi: 10.1083/jcb.95.2.470. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hansen W., Garcia P. D., Walter P. In vitro protein translocation across the yeast endoplasmic reticulum: ATP-dependent posttranslational translocation of the prepro-alpha-factor. Cell. 1986 May 9;45(3):397–406. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(86)90325-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hortin G., Boime I. Inhibition of preprotein processing in ascites tumor lysates by incorporation of a leucine analog. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1980 Mar;77(3):1356–1360. doi: 10.1073/pnas.77.3.1356. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Johnson A. E., Cantor C. R. Elongation factor-dependent affinity labeling of Escherichia coli ribosomes. J Mol Biol. 1980 Apr;138(2):273–297. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(80)90287-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Johnson A. E., Miller D. L., Cantor C. R. Functional covalent complex between elongation factor Tu and an analog of lysyl-tRNA. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1978 Jul;75(7):3075–3079. doi: 10.1073/pnas.75.7.3075. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Johnson A. E., Slobin L. I. Affinity labeling of eukaryotic elongation factors using N epsilon-bromoacetyl-Lys-tRNA. Nucleic Acids Res. 1980 Sep 25;8(18):4185–4200. doi: 10.1093/nar/8.18.4185. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Johnson A. E., Woodward W. R., Herbert E., Menninger J. R. Nepsilon-acetyllysine transfer ribonucleic acid: a biologically active analogue of aminoacyl transfer ribonucleic acids. Biochemistry. 1976 Feb 10;15(3):569–575. doi: 10.1021/bi00648a018. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kozak M. Point mutations close to the AUG initiator codon affect the efficiency of translation of rat preproinsulin in vivo. Nature. 1984 Mar 15;308(5956):241–246. doi: 10.1038/308241a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kurzchalia T. V., Wiedmann M., Girshovich A. S., Bochkareva E. S., Bielka H., Rapoport T. A. The signal sequence of nascent preprolactin interacts with the 54K polypeptide of the signal recognition particle. Nature. 1986 Apr 17;320(6063):634–636. doi: 10.1038/320634a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Melton D. A., Krieg P. A., Rebagliati M. R., Maniatis T., Zinn K., Green M. R. Efficient in vitro synthesis of biologically active RNA and RNA hybridization probes from plasmids containing a bacteriophage SP6 promoter. Nucleic Acids Res. 1984 Sep 25;12(18):7035–7056. doi: 10.1093/nar/12.18.7035. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Meyer D. I., Krause E., Dobberstein B. Secretory protein translocation across membranes-the role of the "docking protein'. Nature. 1982 Jun 24;297(5868):647–650. doi: 10.1038/297647a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miller D. L., Weissbach H. Elongation factor Tu and the aminoacyl-tRNA-EFTu-GTP complex. Methods Enzymol. 1974;30:219–232. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(74)30024-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pingoud A., Block W., Wittinghofer A., Wolf H., Fischer E. The elongation factor Tu binds aminoacyl-tRNA in the presence of GDP. J Biol Chem. 1982 Oct 10;257(19):11261–11267. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sasavage N. L., Nilson J. H., Horowitz S., Rottman F. M. Nucleotide sequence of bovine prolactin messenger RNA. Evidence for sequence polymorphism. J Biol Chem. 1982 Jan 25;257(2):678–681. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Siegel V., Walter P. Elongation arrest is not a prerequisite for secretory protein translocation across the microsomal membrane. J Cell Biol. 1985 Jun;100(6):1913–1921. doi: 10.1083/jcb.100.6.1913. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Walter P., Blobel G. Preparation of microsomal membranes for cotranslational protein translocation. Methods Enzymol. 1983;96:84–93. doi: 10.1016/s0076-6879(83)96010-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Walter P., Blobel G. Signal recognition particle: a ribonucleoprotein required for cotranslational translocation of proteins, isolation and properties. Methods Enzymol. 1983;96:682–691. doi: 10.1016/s0076-6879(83)96057-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Walter P., Blobel G. Subcellular distribution of signal recognition particle and 7SL-RNA determined with polypeptide-specific antibodies and complementary DNA probe. J Cell Biol. 1983 Dec;97(6):1693–1699. doi: 10.1083/jcb.97.6.1693. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Walter P., Blobel G. Translocation of proteins across the endoplasmic reticulum III. Signal recognition protein (SRP) causes signal sequence-dependent and site-specific arrest of chain elongation that is released by microsomal membranes. J Cell Biol. 1981 Nov;91(2 Pt 1):557–561. doi: 10.1083/jcb.91.2.557. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Walter P., Gilmore R., Blobel G. Protein translocation across the endoplasmic reticulum. Cell. 1984 Aug;38(1):5–8. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(84)90520-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Walter P., Ibrahimi I., Blobel G. Translocation of proteins across the endoplasmic reticulum. I. Signal recognition protein (SRP) binds to in-vitro-assembled polysomes synthesizing secretory protein. J Cell Biol. 1981 Nov;91(2 Pt 1):545–550. doi: 10.1083/jcb.91.2.545. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]