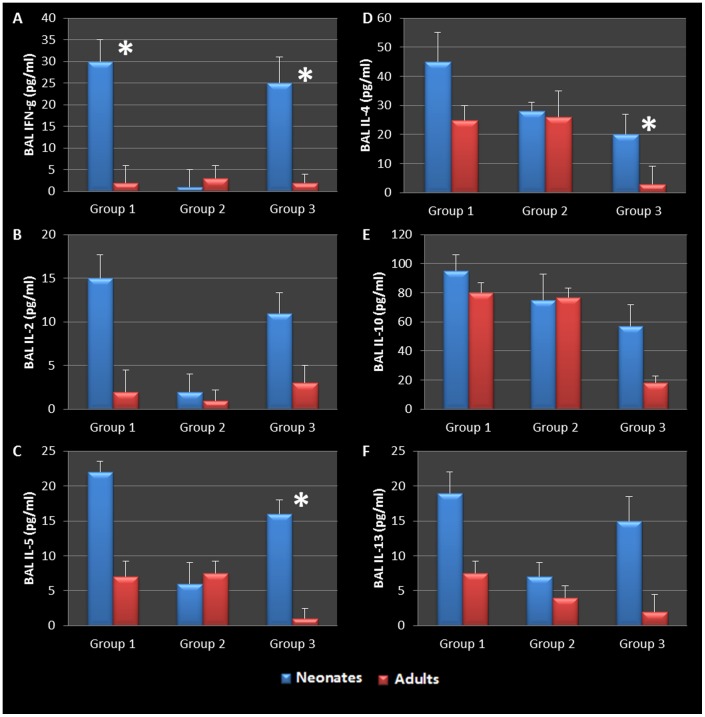
Figure 8. BAL cytokines during allergic airway disease.
Infected adults who cleared infection, developed a mixed Th1/Th2 immune response during allergic airway induction (C-F). Group 1 and 3 infected neonates responded with a significant increase in IFN-g (P = 0.0049, 0.0092 respectively, A) and elevated levels of IL-2 when compared to corresponding adult groups (B). Th2 cytokines that were produced in all groups that had AAD induced (C-F). Infected neonates hyper reacted to ovalbumin compared to their adult and uninfected counterparts. Importantly to note, group 3 neonates who had active infections but no AAD produced significantly elevated amounts of IL-5 and IL-4 (P = 0.0152, 0.0362 respectively C, D) and elevated levels of IL-10, and 13 compared to all other groups (E,F). Collectively, the data therefore suggests that early life chlamydial infection induces an allergic airway response upon allergen challenge that is typical of asthma pathogenesis and supports a chronic infection model airway hyperresponsiveness.