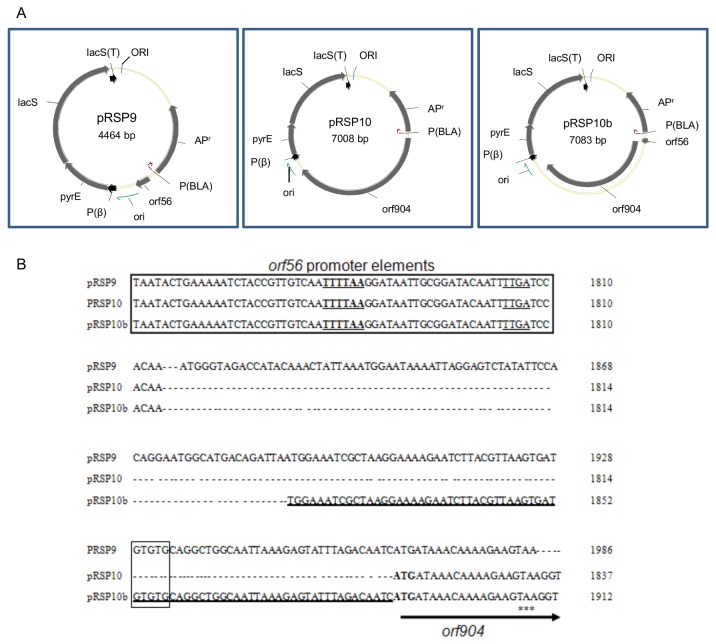
Figure 5. In-trans complementation of orf56 and orf904 deletion mutants of pRSP1.
(A) Deletion mutants of pRSP1 generated by deleting orf904 (pRSP9) and orf56 (pRSP10/pRSP10b) from pRSP1; pRSP10 contained a complete orf904 under the control of orf56 transcription and translation elements, while pRSP10b contained an additional 75-bp at the 5’ of orf904 start codon. Each plasmid contains pUC19 and pRN1 origins of replication, the pyrE-lacS cassette transcribed by the S. solfataricus thsB promoter [P(β)] and lacS terminator element [lacS(T)], and APr gene (ampicillin resistance). (B) Cis-acting elements at the 5’ of orf56 and orf904 in each plasmid. Transcription of orf904 in pRSP10 and pRSP10b is controlled by of orf56 promoter elements (big bold box) with putative TATA box A (bold single underline) and TATA box B (single underline). The 75-bp element 5’of orf904 in pRSP10b (bold underline) contains a putative RBS (small box). The start of orf904 is bolded, and the stop of orf56 is represented by (***).