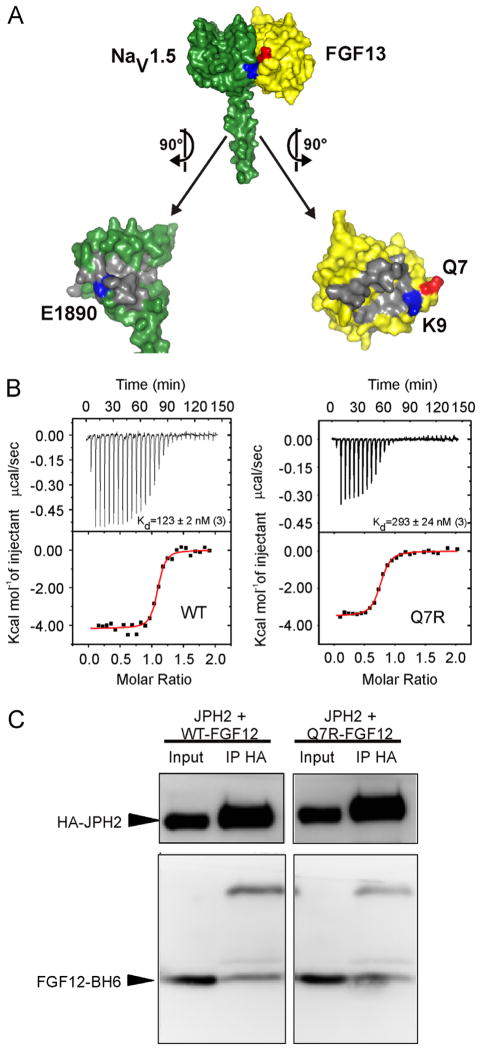
Figure 2.
Q7R-FGF12 decreases affinity for the NaV1.5 CTD. A: Surface rendering of the interface between the NaV1.5 CTD (green) and the FHF core domain (yellow). Q7 (red) is in the same plane as the salt bridge between the NaV1.5 CTD and the FHF core domain, which is made of E1890 in the NaV1.5 CTD and K9 in FGF13 (blue). B: Isothermal titration calorimetry data demonstrate a 2-fold decrease (P < .05) in binding affinity for Q7R-FGF12 versus WT from 3 independent experiments. C: Representative co-immunoprecipitation and Western blot of FGF12-B WT or Q7R with JPH2 from at least 3 independent experiments. CTD = C-terminal domain; FGF = fibroblast growth factor; FHF = fibroblast growth factor homologous factor; HA = XXXX; IP = XXXX; JPH2 = junctophilin-2; WT = wild type.