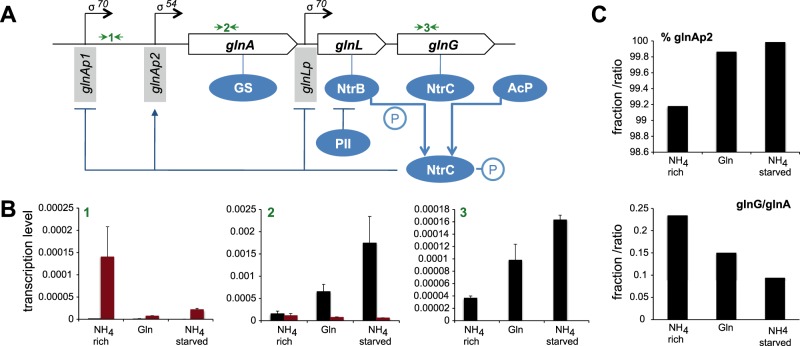
FIG 3 .
Transcription from different NtrC-dependent promoters within the glnALG operon under different nitrogen regimes. (A) Scheme of the glnALG operon architecture and NtrC-mediated feedback loops acting at σ70- and σ54-dependent promoters. Black arrows indicate three primer pairs used for quantitative PCR of glnAp1 (1), glnA (2), and glnG (3). (B) mRNA levels relative to 16 s mRNA of E. coli NCM3722 (black) and NCM3722ΔglnG (red) strains comprising glnAp1 (1), glnA (2), and glnG (3) message. Transcript levels between E. coli NCM3722 and NCM3722ΔglnG strains confirm the regulatory roles of NtrC at those promoters. (C) The percentage of glnAp2 activity of total glnA transcription was derived from glnA transcripts minus glnAp1 transcripts. The ratio of glnG transcripts relative to glnA transcripts reflects on the regulation at the glnLp promoter.