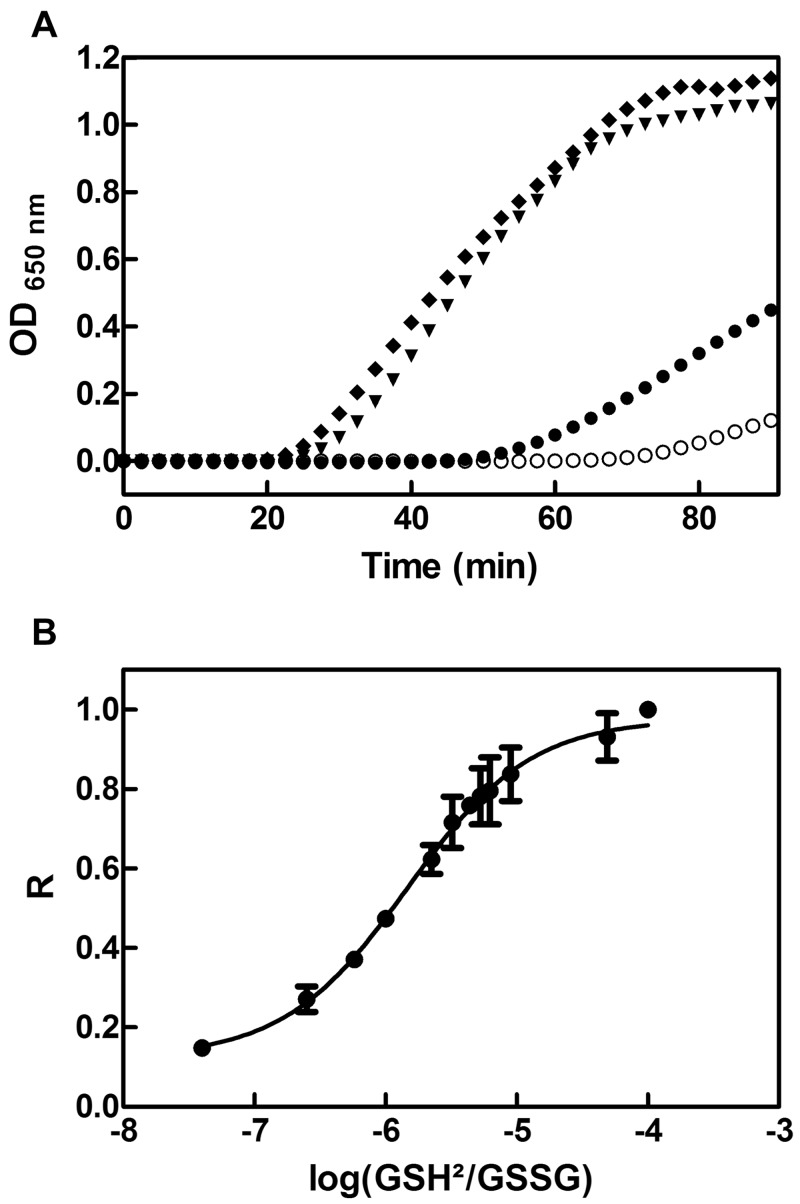
FIG 4 .
PaDsbA2 is an oxidoreductase with a highly oxidizing redox potential. (A) We tested the ability of PaDsbA2 to function as an oxidoreductase by measuring its ability to catalyze the reduction of insulin by DTT. Insulin (150 µM) was incubated with 10 µM of either PaDsbA1 (▼), PaDsbA2 (●), or EcDsbA (♦). The noncatalyzed reaction (DTT alone; ○) was also monitored. DTT (0.8 mM) was added at time zero, and the reduction of insulin was measured by monitoring the increase in absorbance at 650 nm. The data shown are averages of three independent experiments. (B) We determined the redox potential of PaDsbA2 by equilibrating the protein in redox buffers containing different GSH/GSSG ratios. The redox potential was calculated from the ratio (R) between the amounts of oxidized and reduced PaDsbA2 present at equilibrium and determined using AMS trapping experiments. The data shown are averages (± standard deviations [error bars]) of three independent experiments.