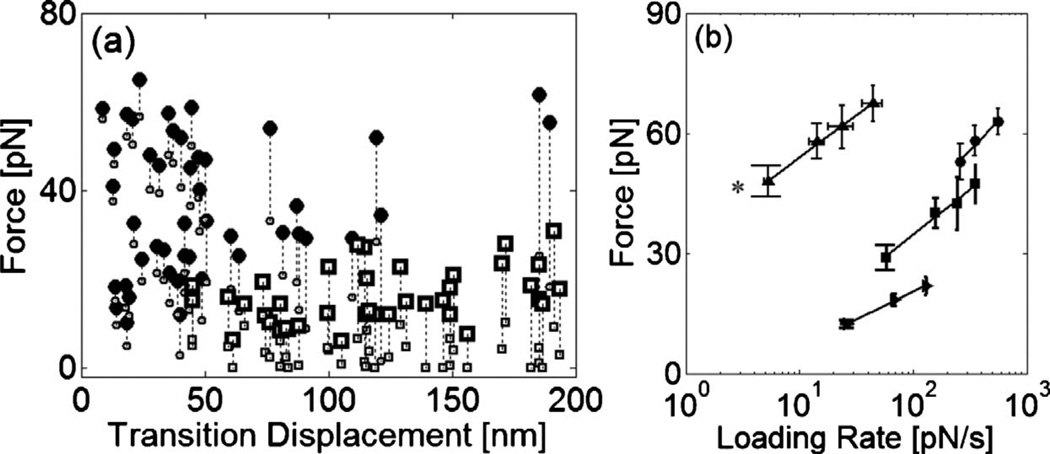
FIG. 3.
(a) Relation of force and displacement at the transitions exhibited in the responses of the F-actin gels to linear bead displacement. For the filamin/F-actin network (●), the transitions occur at a force of 37±17 pN with a displacement of 29±17 nm. In contrast, for the entangled F-actin solution (□), they are observed at a lower force of 21±6.1 pN with larger displacement, 117±49 nm. Small symbols indicate forces after transition. (b) Dependence of transition force on loading rate for the F-actin solution (►), filamin/F-actin network (■), streptavidin/biotin-F-actin network (●). Rupture forces for actin gels increases as the loading rates increase. As the strength of cross-linker increases, the network rupture is observed at the higher force. Forces at the transitions observed in the filamin/F-actin networks’ responses exhibit a similar loading rate dependence of slope to unbinding force (▲) between a single filamin and F-actin. (*Results adapted from Ref. [12])