Figure 2.
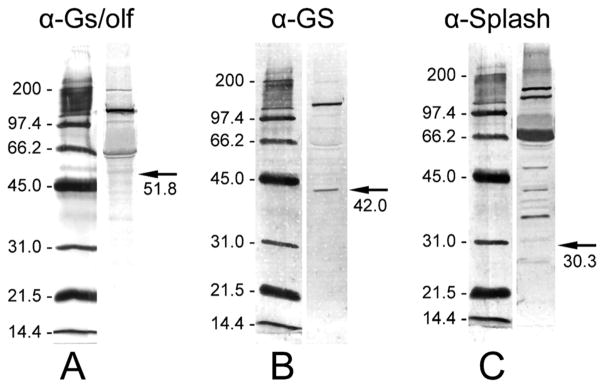
Western blot analyses of total proteins extracted from P. argus brains with three antibodies used for the immunocytochemical characterization of the neurogenic complexes. Left: Alkaline-phosphatase-labeled molecular mass markers (indicated in kDa) visualized by NBT/BCIP running in the same SDS-PAGE gel as the antibody-labeled brain extract. Right: 10 μg P. argus brain extract labeled by one of the antibodies used for immunocytochemistry followed by detection through a secondary antibody labeled with alkaline phosphatase and its visualization by NBT/ BCIP. Arrows indicate the expected molecular mass (given below in kDa) of the target protein. A: Labeling with anti-Gs/olf revealed a double-band at an apparent molecular mass of ~61/63 kDa, a very prominent band at ~137 kDa, and a weak band at ~200 kDa. Gs cloned from the American lobster H. americanus has a molecular mass of ~51.8 kDa (Xu et al., 1997). B: Labeling with anti-GS revealed one band at the expected molecular mass of ~42 kDa that was reported for GS cloned from P. argus (Linser et al., 1997) and an additional very prominent band at ~136 kDa. C: Labeling with anti-Splash revealed at least six prominent bands at apparent molecular masses above the predicted molecular mass (30.3 kDa) of P. argus Splash (Chien et al., 2009).
