Figure 5.
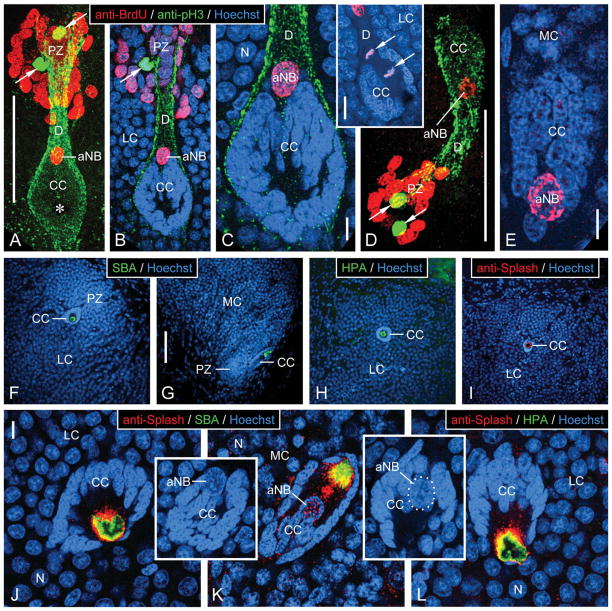
Characterization of neurogenic complexes in the lateral and medial soma cluster by fluorescent labeling. A–E: Triple labeling with anti-BrdU, anti-pH3, and Hoechst 33258 after a single BrdU injection in the morning and 6 hours of survival time. Inset: Double labeling with anti-BrdU and Hoechst 33258. Micrographs represent collapsed stacks or substacks of optical sections (thickness 0.3–1.5 μm) from 80-μm-thick sections taken with a two-photon confocal microscope at three excitation wavelengths to visualize anti-BrdU (red), anti-pH3 (green), and Hoechst 33258 (blue). A–C: Lateral soma cluster (LC). D,E: Medial soma cluster (MC). A,D: Micrographs representing the entire section thickness omitting the Hoechst-33258 channel for clarity. A dense group of small BrdU+ nuclei occupies the proliferation zone (PZ). Few pH3+ nuclei (arrows) are located within the group of BrdU+ nuclei. The proliferation zone is connected by a duct whose outer layer consists of fibrous pH3+ material (D) to the clump of cells (CC), which at its PZ-facing pole contains the large BrdU+ nucleus of an adult neuroblast (aNB). Note a nucleus- and label-free hole in the center of the clump of cells (asterisk in A) representing the bulbous foot of the aNB. B,C,E: Micrographs representing collapsed stacks of two (B), three (C, inset), or five (E) optical sections with a total thickness of 0.7 μm (B), 0.9 μm (C, inset), or 1.5 μm (E). The clump of cells (CC) consists of a cortex of small and densely packed nuclei of clump-forming cells that differ distinctly in size and shape from the BrdU+ nucleus of the adult neuroblast (aNB) and from the nuclei of mature or maturing neurons (N). B,C: The clump of cells is surrounded by a layer of pH3+ fibrous material that is contiguous with the material forming the outer layer of the duct (D) connecting with the proliferation zone (PZ). Note that a pH3+ nucleus in the proliferation zone (arrow in B) is not BrdU+, indicating that it was not in S-phase when BrdU was present. Inset: aNB captured in telophase of mitosis. Note that the mitotic plane is perpendicular to the long axis of the clump of cells and duct; condensed daughter nuclei (arrows). F–L: Labeling with lectins and anti-Splash demonstrating that the bulbous foot of the adult neuroblast is immunocytochemically privileged. Micrographs represent collapsed stacks or substacks of optical sections (thickness 0.3–1.5 μm) from 80-μm-thick sections taken with a two-photon confocal microscope at two or three excitation wavelengths to visualize Hoechst 33258 (blue) and anti-Splash (red), SBA (green), or HPA (green). F–I: Micrographs at low magnification demonstrate that in the lateral soma cluster (LC; F,H,I) and in the medial soma cluster (MC; G), SBA (F,G), HPA (H), and anti-Splash (I) selectively label the center of the clump of cells (CC) containing the bulbous foot of the adult neuroblast. J–L: Micrographs at higher magnification reveal that the lectin+ area in the nucleus-free center of the clump of cells (CC) is surrounded by Splash+ material. Note that the large nucleus of the adult neuroblast (aNB; in insets on different optical sections with the same orientation as in J and L; in inset K, nucleus of adult neuroblast outlined by white dots) is located at the pole of the clump of cells opposing the nucleus-free center. Scale bars = 100 μm in A (applies to A,B); 10 μm in C,E; 20 μm in C inset; 100 μm in D; 100 μm in G (applies to F–I); 10 μm in J (applies to J–L, J,K insets).