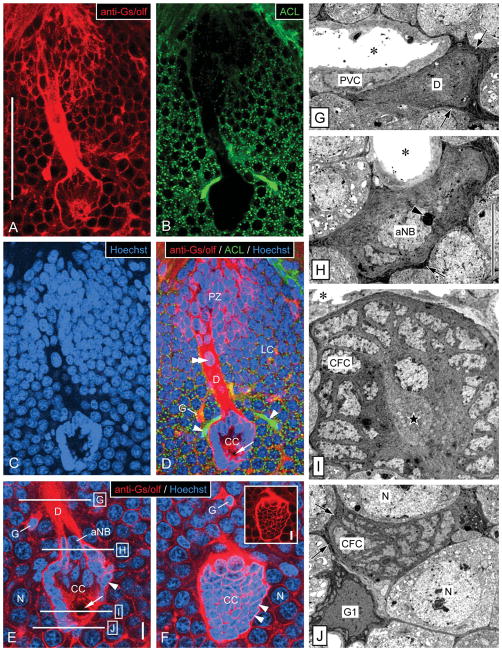
Figure 6.
Overview of ultrastructure of the neurogenic complex in the lateral soma cluster by correlation of fluorescent labeling and TEM. A–F: Fluorescent labeling of a sagittal vibrating-microtome section through the neurogenic complex in the lateral soma cluster (LC) with anti-Gs/olf (red in A,D–F), ACL (green in B,D), and Hoechst 33258 (blue in C–F). Micrographs represent collapsed stacks of eight (A–D) or three (E,F) optical sections with a total thickness of 5.6 μm (A–D) or 0.9 μm (E, F). A–D: Low magnification reveals the spatial correlation of the three main components of the neurogenic complex: proliferation zone (PZ), clump of cells (CC), and duct (D) connecting them. The neurogenic complex stands out from the neuronal somata in its surround by being more intensely labeled by anti-Gs/olf (A), by being ACL− (B), and by having a unique arrangement of cell nuclei (C). Note that ACL intensely labels arterioles (asterisks) one of which is attached to the clump of cells, that anti-Gs/olf also intensely labels cell body glia (G), that the nucleus-free center of the clump of cells contains a round area devoid of Gs/olf-like immunoreactivity (arrow), and that the duct contains a large oval nucleus (double arrowhead). E,F: Higher magnification reveals the organization of the clump of cells (CC) at two levels of one stack of optical sections. E: Section through the midplane of the clump of cells. Small nuclei of clump-forming cells (arrowhead) form a dense cortex around a nucleus-free center that contains a round area that is Gs/olf− (arrow). At the origin of the duct (D), the clump-forming cells (CFC) surround the large oval nucleus of the adult neuroblast (aNB). A cell body glial cell (G) has a denser nucleus than surrounding neurons (N), and one of its Gs/olf+ processes connects with the duct. Approximate levels of TEM cross-sections through the duct and clump of cells (G,H) indicated by horizontal lines. F: Section through the cortex of the clump of cells. The cortex of the clump of cells is formed by closely associated somata of clump-forming cells (arrowheads) that have very little cytoplasm (inset: Hoechst signal omitted for clarity) surrounding their dense nucleus. The clump of cells is surrounded by neuronal somata (N) and interspersed Gs/olf+ cell body glia (G). G–J: Low-magnification TEM micrographs of cross-sections through the duct and the clump of cells in the lateral soma cluster at levels indicated in E. G: Cross-section through the duct. The duct (D) is a massive strand of tissue composed of the distal processes of clump-forming cells and is surrounded by a layer of electron-dense processes of cell body glia (arrows). A large arteriole whose lumen (asterisk) is surrounded by processes of perivascular cells (PVC) is attached to the duct. H: Cross-section through the apex of the clump of cells. Processes of clump-forming cells (CFC) form a thick continuous layer around the peripheral domain of the adult neuroblast (aNB) characterized by a large nucleus with a large, peripheral nucleolus (arrowhead; arrows, layer of electron-dense processes of cell body glia surrounding the clump of cells; asterisk, lumen of attached arteriole). I: Cross-section through the center of the clump of cells. Somata of clump-forming cells (CFC) form a dense cortex around a nucleus free center filled by their inner processes and the bulbous foot of the adult neuroblast (star; asterisk, lumen of attached arteriole). J: Cross-section through the bottom of the clump of cells. The contiguous cortex of the clump of cells formed by somata of clump-forming cells (CFC) is surrounded by a layer of electron-dense processes of cell body glia (arrows) some of which are contributed by a type 1 cell body glia in the immediate vicinity (G1). N, neuronal soma. Scale bars 100 μm in A (applies to A–D); 10 μm in E (applies to E,F); 10 μm in inset; 10 μm in H (applies to G–J).