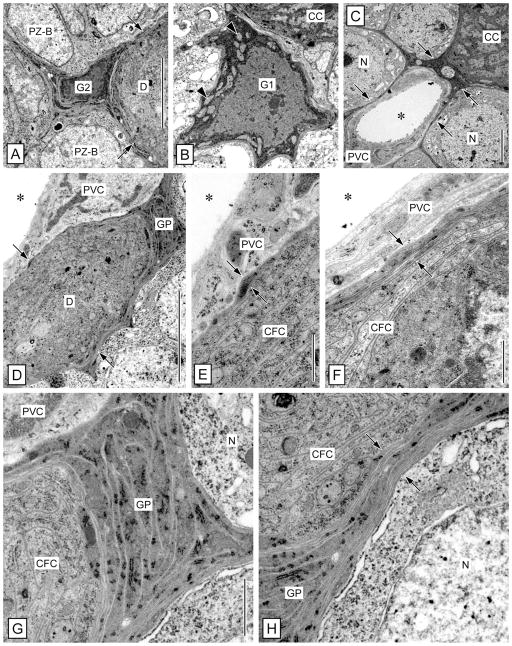
Figure 8.
Ultrastructure of the clump of cells and duct: glial sheath and association with arteriole. TEM micrographs of cross-sections through the duct or the clump of cells in the lateral soma cluster. A: Type 2 cell body glia (G2) closely associated with the duct (D). From the soma of the type 2 cell body glia, processes extend between surrounding type B proliferation zone cells (PZ-B) and contribute to the glial sheath surrounding the duct (arrows). B: Type 1 cell body glia (G1) closely associated with the clump of cells (CC). Note multipolar morphology of the soma and numerous electron-lucent mitochondria (arrowhead) in the electron-dense cytoplasm. C: Arteriole attached to the clump of cells. A simple arteriole with a lumen (asterisk) surrounded by a layer of processes of perivascular cells (PVC) is separated from neuronal somata (N) and from the clump of cells (CC) by a continuous layer of electron-dense processes of cell body glia (arrows). D–F: Separation of duct and clump of cells from the attached arteriole. D,E: The outer processes of clump-forming cells (CFC) that constitute the duct (D) are surrounded by a layer of electron-dense processes of cell body glia (GP; arrows). Only one process of cell body glia (opposing arrows in E) separates the CFC processes from the perivascular cell (PVC) surrounding the lumen of the attached arteriole (asterisk). F: At the clump of cells, several processes of cell body glia (opposing arrows) separate the clump-forming cells (CFC) from the perivascular cell processes (PVC) surrounding the lumen of the attached arteriole (asterisk). G,H: Separation of duct and clump of cells from neuronal somata. G: A thick accumulation of numerous processes of cell body glia (GP) is interspersed between the outer processes of clump-forming cells (CFC) forming the duct and adjacent neuronal somata (N). H: At the clump of cells, multiple processes of cell body glia (GP; opposing arrows) separate the clump-forming cells (CFC) from adjacent neuronal somata (N). Scale bars = 5 μm in A (applies to A,B); 5 μm in C,D; 1 μm in E,F; 1 μm in G (applies to G,H).