FIGURE 1. Pro-apoptotic chemotherapeutic drugs induce the release of IL-1β in LPS-primed murine bone marrow-derived dendritic cells (BMDC).
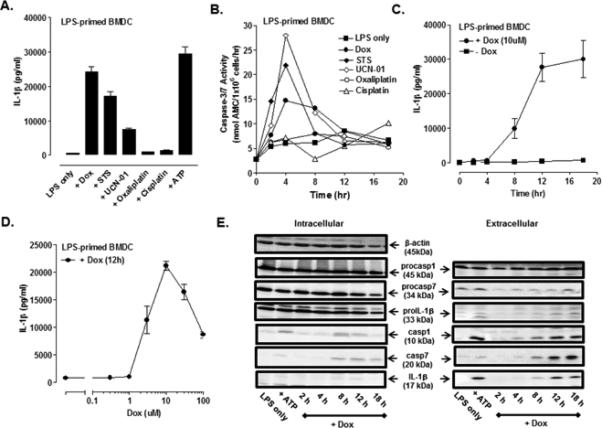
(A) BMDC were primed with LPS (1μg/ml) for 4 h prior to stimulation for 12 h with a panel of pro-apoptotic agents including staurosporine (STS, 5 μM), UCN-01 (10 μM), doxorubicin (Dox, 10 μM), oxaliplatin (Ox, 25 μM) and cisplatin (CDDP, 25 μM). The extracellular medium was collected and assayed for IL-1β by ELISA. BMDC were primed with LPS for 15.5 h prior to ATP (5mM) stimulation for 30 min. Results are the mean ± range of two experiments. (B) The kinetics of drug-induced caspase-3/7 activity in LPS-primed BMDC was measured by proteolytic cleavage of the DEVD-AMC substrate. The concentrations of each drug used were the same as described in (A). Results are from a single experiment. (C) The kinetics of IL-1β release from LPS-primed and Dox-stimulated (10 μM) WT BMDC were assayed by ELISA. Results are the mean ± SE from 4-8 experiments. (D) LPS-primed BMDC were stimulated with varying doses of Dox for 12 h. Results are the mean ± SE of 3 experiments. (E) WT BMDC were stimulated as in (C), and the extracellular medium and cell lysates were collected and processed for western blot analysis for detection of IL-1β, caspase-1, and caspase-7. BMDC were primed with LPS for 5.5 h prior to ATP (5mM) stimulation for 30 min. The data are representative of results from 3 experiments.
