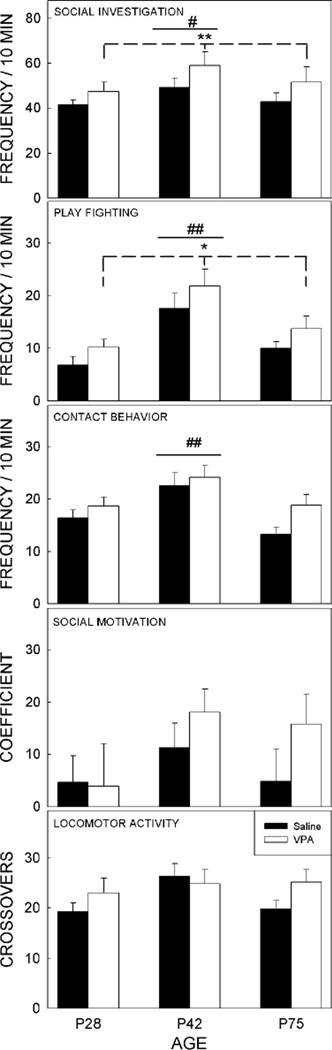
Figure 1.
Effects of Exposure to Valproic Acid on Social Behavior.
Four features of social behavior as well as locomotor activity were analyzed from a modified social interaction test. Both social investigation and play fighting, were significantly increased in animals exposed to valproic acid when the data were collapsed across age. Three features, social investigation, play fighting, and contact behavior, were significantly increased in 42-day-old animals compared with those tested on P28 or P75 (data collapsed across treatment). Neither social motivation nor locomotor activity showed a significant effect of age or prenatal treatment.
Significant differences between saline- and valproic acid-exposed animals: * p < 0.05, ** p<0.01. Significant differences between age groups: # p < 0.01, ## p<0.001. Bars show the mean for each group, t-bars depict the standard error of the mean. No differences between the sexes were identified for any of the measures, thus data were collapsed across sex.