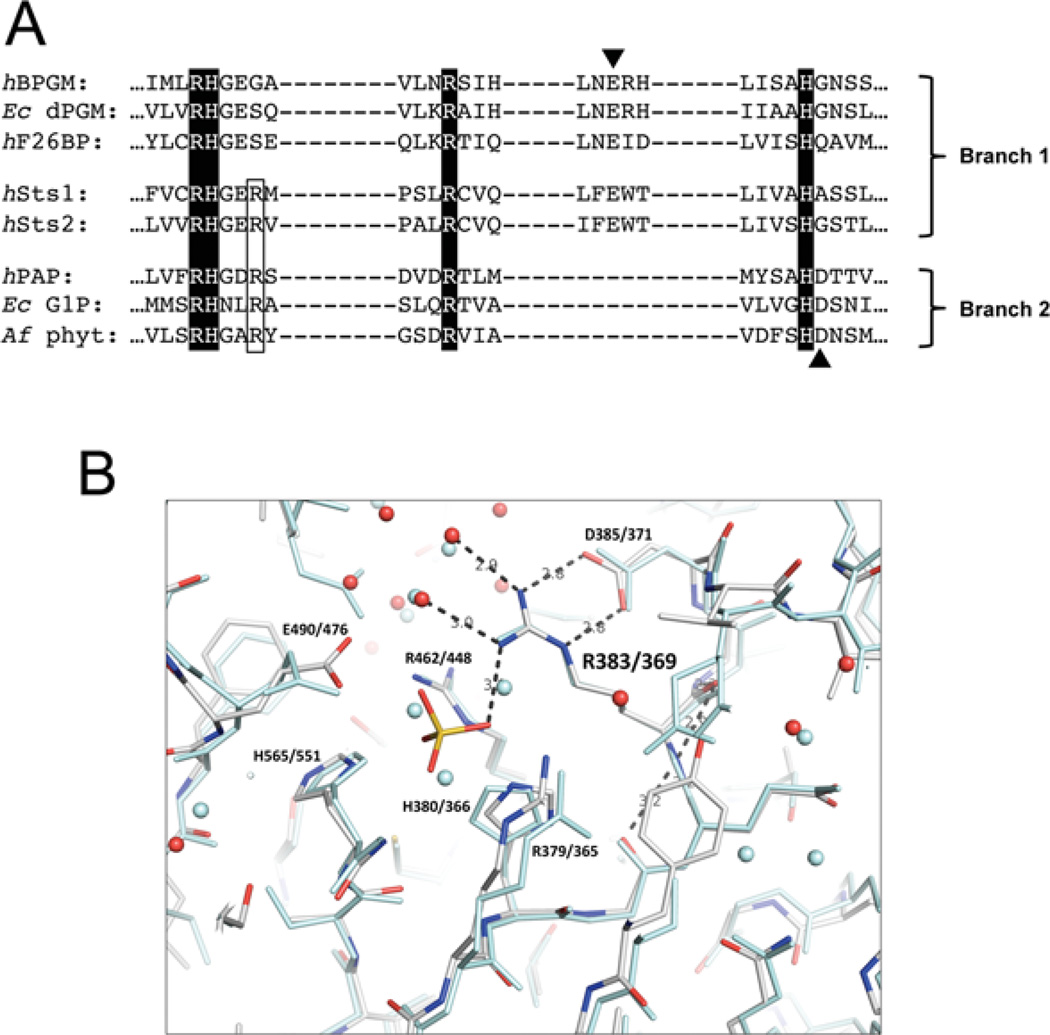
Figure 1. Presence of a conserved arginine residue alongside the catalytic quartet in the Sts-1 active site.
(A) Sts phosphatase domain sequences were aligned with sequences of enzymes representing the PGM and AcP branches of the HP superfamily: human bisphosphoglycerate mutase (hBPGM), Escherichia coli cofactor-dependent PGM (Ec dPGM), human fructose-2,6-bisphosphatase (hF26BP), human prostatic acid phosphatase (hPAP), E. coli glucose-1-phosphatase (Ec G1P) and Aspergillus fumigatus phytase (Af phyt). The invariant catalytic quartet residues are highlighted and the acidic residues that are thought to act as proton donors during the second step of the catalytic reaction are indicated with arrowheads. The conserved arginine residue that is the subject of this study is outlined. (B) Superimposition of Sts-1 and Sts-2 active sites, illustrating hydrogen-bond interactions between Arg383/369 (Sts-1/Sts-2) and elements within the catalytic pocket. The phosphate molecule is derived from phosphate buffer in which crystals were soaked. Sts-1 residues are rendered in colour and those of Sts-2 are in pale blue.