Figure 1. Mechanism of anthracycline toxicity within the cardiomyocyte.
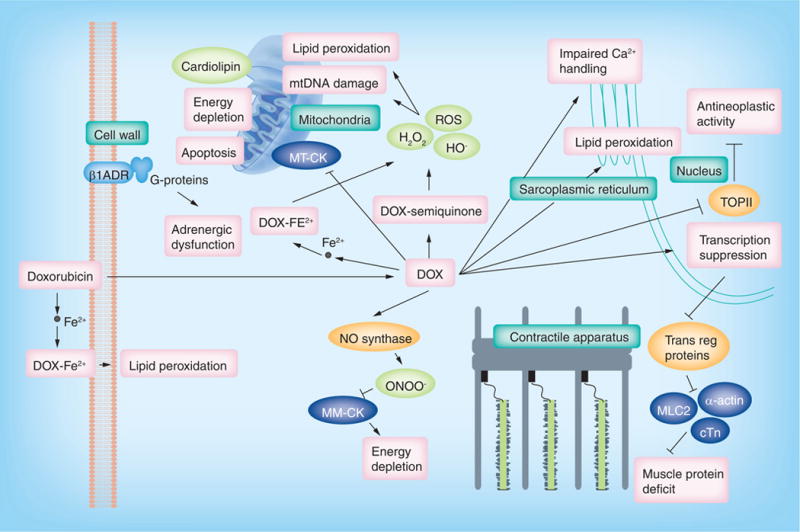
Anthracyclines enter cardiomyocytes by passive diffusion and spur the generation of free radicals, leading to cell damage. Anthracyclines also directly and indirectly inhibit gene transcription, mitochondrial functioning, and energy production within the cell.
β1ADR: β1 adrenergic receptor; Ca: Calcium; cTn: Cardiac troponin; DOX: Doxorubicin; Fe2+: Iron; MLC2: Myosin light chain; MM-CK: Muscular creatine kinase; MT-CK: Mitochondrial creatine kinase; NO: Nitric oxide; ROS: Reactive oxygen species; TOPII: Topoisomerase II; Trans reg: Transcriptional regulatory.
Reproduced with permission from [28].
