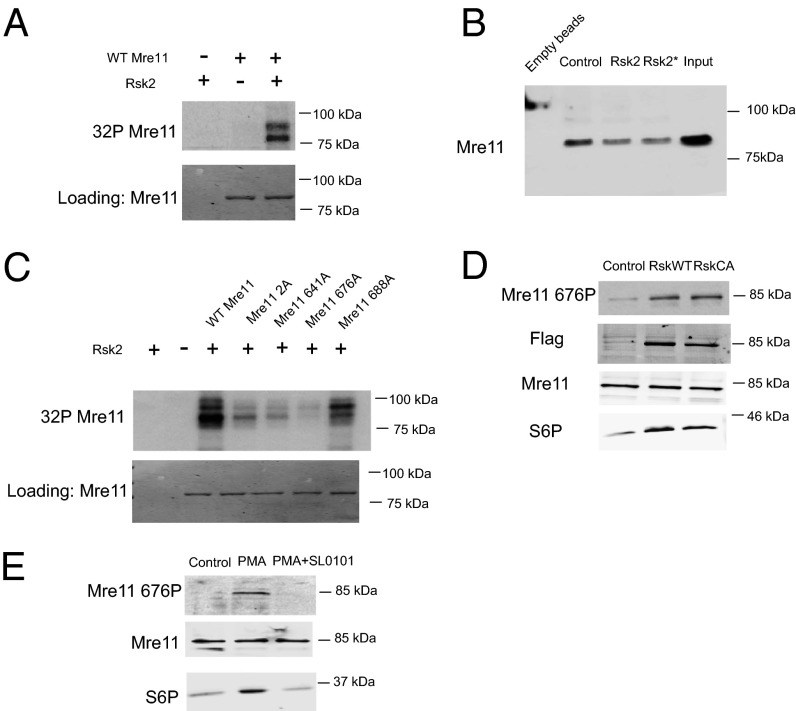
Fig. 4.
Rsk phosphorylates Mre11 at S676. (A) Purified Mre11 protein was treated with Rsk and radiolabeled ATP (in kinase buffer), and labeled proteins were subjected to SDS/PAGE and autoradiography. (B) His-tagged Mre11 protein was phosphorylated in vitro using RSK kinase and added to Xenopus egg extracts for 10 min. Biotin-tagged dsDNA was used to pull down Mre11, and samples were analyzed for Mre11/dsDNA interaction by His-immunoblotting. In one sample (Rsk*), SL0101 and phosphatase inhibitors were added to extracts to prevent further phosphorylation by Rsk or dephosphorylation by phosphatases. (C) Equal amounts of His-tagged Mre11 protein and mutants were treated as in A. (D) Lysates from 293T cells transfected with WT or constitutively active (CA) Rsk were analyzed for endogenous S676 phosphorylated Mre11 by immunoblotting with phospho-specific antibody. (E) Lysates from 293T cells treated with PMA ± SL0101 were analyzed for endogenous S676 phosphorylated Mre11 by immunoblotting with phospho-specific antibody.