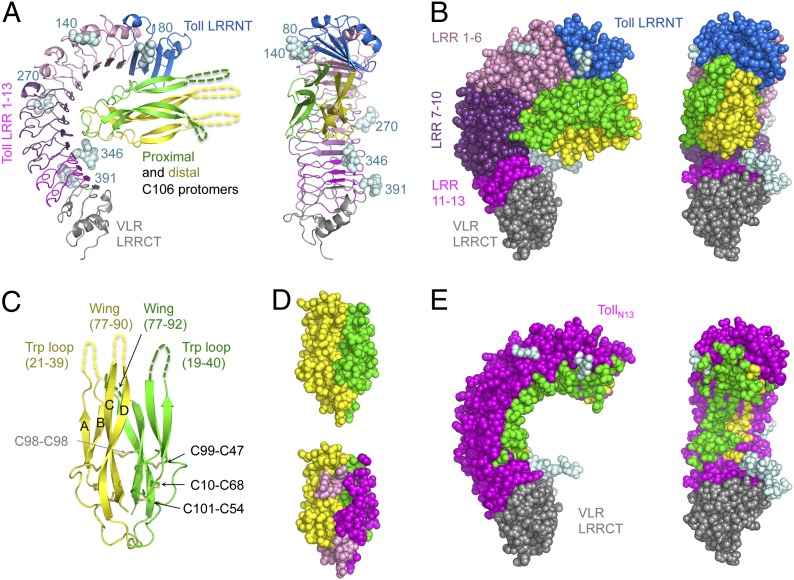
Fig. 1.
Toll–Spz overall structure and ligand binding mode. (A) Schematic representation in two orientations (side view and concave view) with color-coded areas for Toll and Spz C106 dimer. The first N-acetylglucosamine residue of the glycan structures attached to Asn residues at positions 80, 140, 270, 346, and 391 is shown in light cyan spheres. (B) Space-filling models highlight the spatial restriction provided by the presence of the glycosylations. (C) Schematic representation of Spz C106 with the four-stranded antiparallel β-sheet labeled A–D and the two missing regions, the Trp loop, and the wing of each protomer indicated by dashed lines and corresponding missing residue numbers. The disulfide bonds of the cystine residues involved in the knot motif are shown along with the intermolecular bond involving Cys-98 of each chain. (D) Space-filling model of the Spz cystine-knot domain as observed in the complex structure, color-coded by polypeptide chain in Upper. In Lower, the same orientation highlights the footprint left by Toll across the dimeric surface of the ligand (interface colored in magenta for the proximal chain and pink for the distal one). (E) The asymmetry of the binding to Toll is represented by color-coding Toll residues that interact with Spz in either green or yellow depending on which chain that they contact.