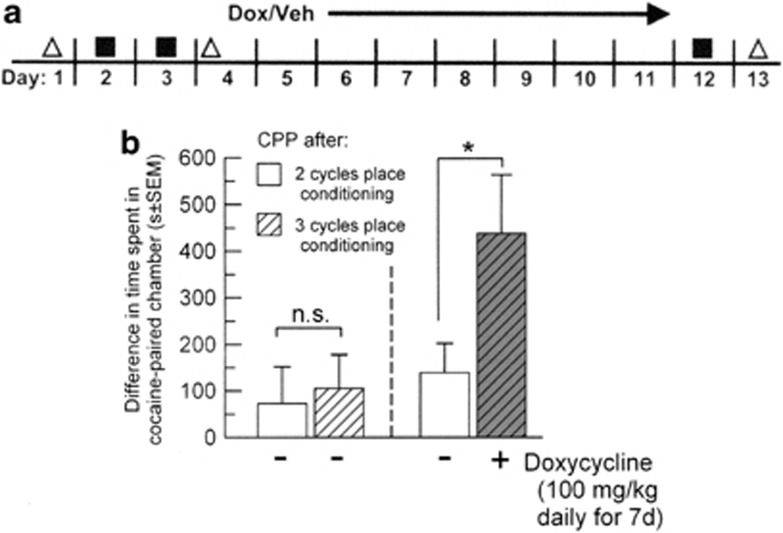
Figure 3.
Induction of Tat potentiated the reward associated with previously established, cocaine-conditioned place preference (CPP). (a) Schematic of experimental design. Uninduced GT-tg bigenic mice were tested for place preference (triangles) the days before and after place-conditioning with cocaine and saline for 2 days (squares). Mice were then either administered doxycycline (Dox) to induce Tat expression or control vehicle (Veh) daily for 7 days. Treated mice were given an additional cycle of conditioning (day 12) and re-tested for place preference (day 13). (b) Dox treatment potentiates a previously established CPP after an additional cycle of place-conditioning. Both groups of uninduced mice demonstrated equivalent post-conditioning cocaine preference (open bars). Vehicle-treated mice given an additional cycle of conditioning demonstrated no change in cocaine place-preference (striped white bar to the left of dashed line). However, Tat-induced mice displayed a post-induction cocaine-CPP (striped gray bar) that was significantly potentiated from both the previous matching group preference (striped white bar to the left of dashed line) and the preference of the vehicle-treated uninduced mice (solid white bar to right of dashed line). *Indicates significant difference from uninduced GT-tg bigenic mice, p<0.05; NS, no significant difference between groups, one-way analysis of variance (ANOVA).