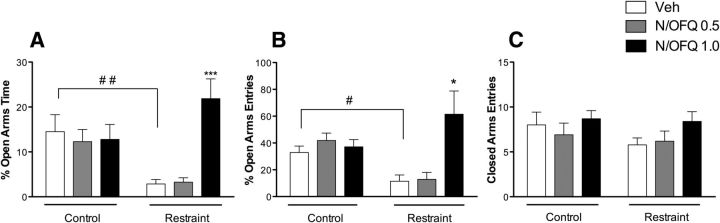
Figure 5.
Effect of intra-CeA N/OFQ (0.0, 0.5, and 1.0 nmol/rat) injection on EPM test. A, Time spent in open arms. ##p < 0.01, Veh control versus Veh restraint (Newman–Keuls post hoc test). ***p < 0.001, N/OFQ 1.0 nmol versus Veh in the restraint group. B, Open arms entries. #p < 0.01, Veh control versus Veh restraint (Newman–Keuls post hoc test). *p < 0.05, N/OFQ 1.0 nmol versus Veh. C, Closed arm entries. The number of closed arm entries was not affected by the restraint procedure or N/OFQ treatment. In summary, our data show higher anxiety-like responses in restraint compared with unrestraint rats. N/OFQ significantly attenuated the effect of restraint stress on anxiety-like responses. Data are mean ± SEM (n = 9 or 10 rats/group).