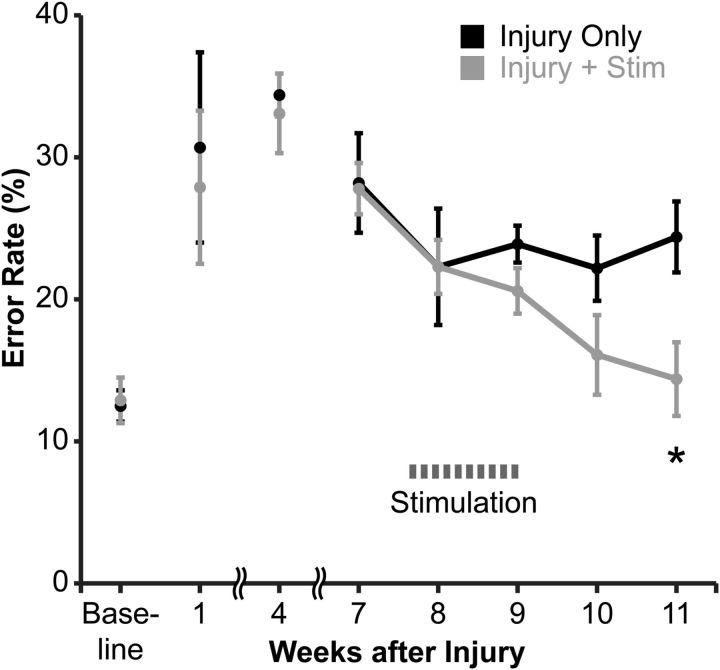
Figure 2.
M1 electrical stimulation after chronic injury improves promotes recovery of skilled walking in the impaired forelimb. Rats were trained to cross a horizontal ladder with irregularly spaced rungs until they achieved a baseline error rate n = 5 per group). Until the start of stimulation (weeks 1–7), the error rates in the two groups were not different. After the start of stimulation (weeks 8–11), the groups differed significantly (repeated-measures ANOVA, with Bonferroni's post hoc correction, *p = 0.03).