Figure 4.
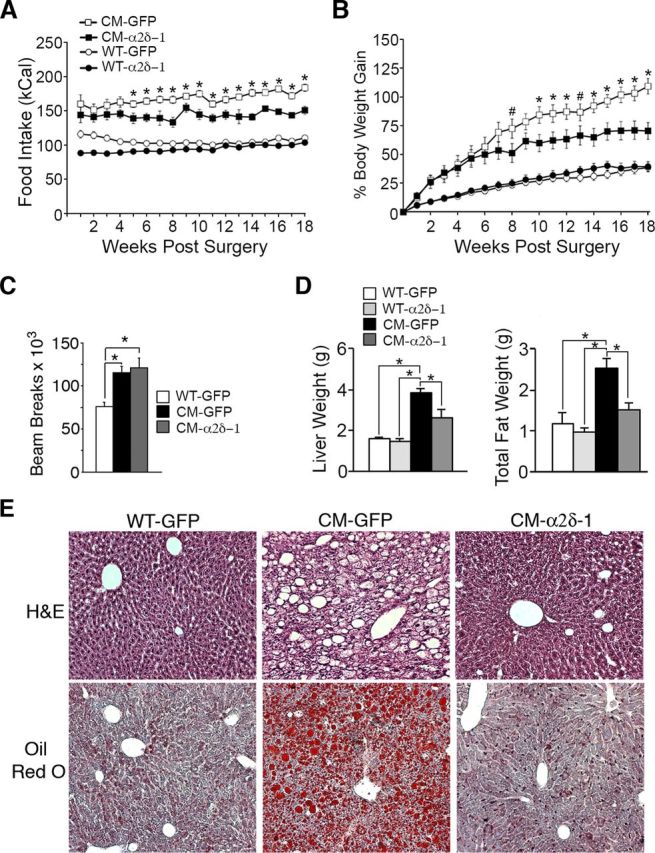
The α2δ-1 rescue in the VMH of BDNF2L/2LCk-cre mutants mitigates their hyperphagia, excessive weight gain, and liver steatosis. A, Weekly food intake of BDNF2L/2LCk-cre conditional mutant mice with VMH delivery of AAV-α2δ-1 (CM-α2δ-1) or AAV-GFP (CM-GFP) and WT mice delivered AAV-α2δ-1 (WT-α2δ-1) or AAV-GFP (WT-GFP). There was a significant effect of time on food intake (F(17,25) = 3.175; p = 0.004, two-way ANOVA with repeated measures; n = 9–12). *p < 0.05, CM-α2δ-1 relative to CM-GFP. B, There was also a significant effect on relative body weight gain (F(18,24) = 53.15; p < 0.00001, two-way ANOVA with repeated measures; n = 9–12). *p < 0.05; #p < 0.1; CM-α2δ-1 relative to CM-GFP. C, Measurement of locomotor activity over 3 d expressed as total beam breaks. *p < 0.01. D, There was a significant effect of treatment on liver (F(3,21) = 70.4; p < 0.001, one-way ANOVA) and total fat (F(3,21) = 17.0; p < 0.001, one-way ANOVA) tissue weights. *p < 0.05. E, Representative liver tissue sections from WT-GFP, CM-GFP, and CM-α2δ-1 mice stained with hematoxylin and eosin (H&E) or Oil Red O, which stains lipids.
