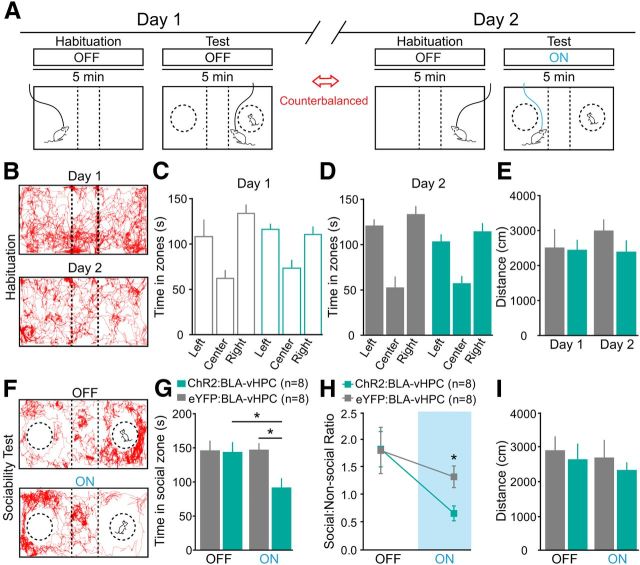
Figure 4.
Activation of BLA projections to the vHPC with ChR2 decreases sociability in a three chamber sociability test. In a different group of animals from Figure 3, glutamatergic neurons from the BLA were transduced with either ChR2-eYFP (n = 8) or eYFP control (n = 8). After ∼6–7 weeks of viral transduction of BLA cell somata, blue light was delivered (5 min, 20 Hz, 5 ms pulses) via unilateral optical fiber implanted in the vHPC. A, Top, Timeline across 2 d of testing. Bottom, Schematic indicating the three chamber sociability test and 5 min experimental epochs. Each testing day was composed of habituation to the arena followed by 5 min of laser ON or laser OFF stimulation (counterbalanced for order). Different juvenile mice were used for each testing epoch, counterbalanced for side of the testing arena. B, Representative animal tracks during the habituation phase for day 1 (top) and day 2 (bottom). C, Time spent in the different zones of the arena during day 1. No significant differences were found between the times spent on the right chamber versus the left chamber. D, Time spent in the different zones of the arena during day 2. No significant differences were found between the times spent on the right chamber versus the left chamber. E, No significant effect on locomotion during the habituation phase during the 2 d of testing. F, Representative animal tracks during the testing sessions for OFF (top) and ON (bottom). G, ChR2 mice spent significantly less time (seconds) in the social zone relative to eYFP mice during the blue light illumination epoch. *p = 0.033. H, ChR2 also showed a significantly lower social/nonsocial ratio during laser stimulation compared with eYFP mice. *p = 0.023. I, No significant effect of locomotion during the habituation phase during the laser stimulation. Data are mean values; error bars indicate ± SEM.