Figure 7.
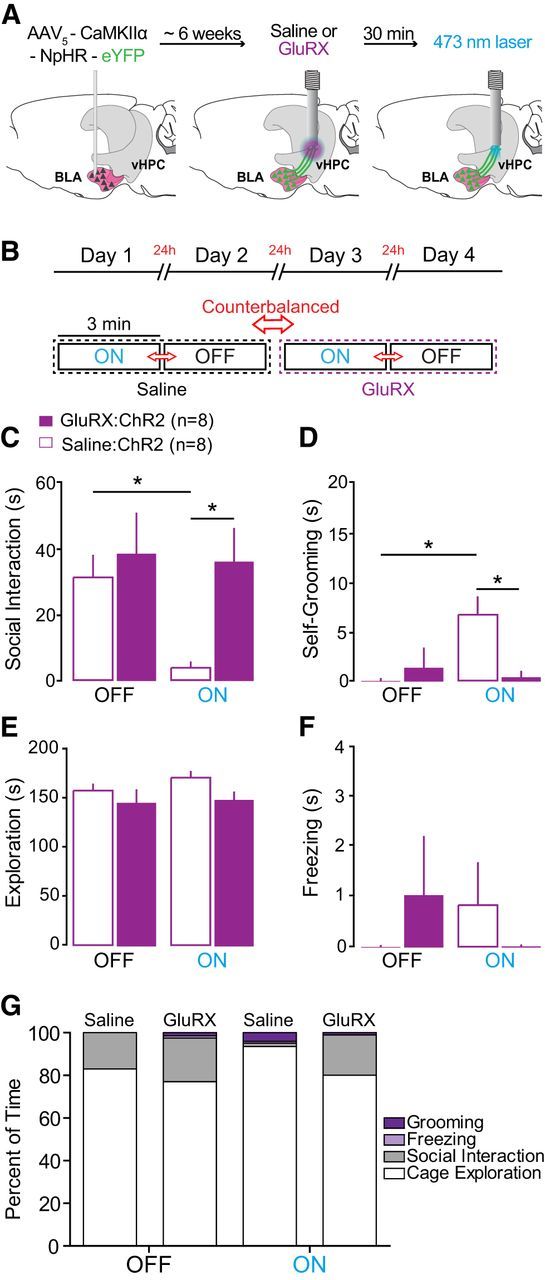
Activation of BLA inputs to the vHPC is sufficient to mediate changes in social interaction without affecting the ability to explore the environment. A, Glutamate receptor antagonists (GluRX:AP5+NBQX, purple) or saline (black) were unilaterally infused into the vHPC using the same guide cannula subsequently used for light delivery via an acutely inserted optical fiber. Top, Experimental timeline. Left, Sagittal brain schematic indicating viral injections into the BLA. Middle, Sagittal schematic indicating unilateral cannula location into the vHPC. Right, Sagittal schematic of removable optical fiber used for light delivery 30 min after GluRX delivery. B, Top, Testing took place over 4 consecutive days. Schematic of 3 min epochs where mice received either drug or saline treatment. All experiments where counterbalanced for treatment and stimulation (ON or OFF epoch) order. Novel juvenile intruders were used for each session. C, GluRX attenuated the light stimulation effect. GluRX:ChR2 mice (n = 8) spent significantly more time (seconds) performing social interaction than Saline:ChR2 mice (n = 8) during the blue light illumination epoch. *p = 0.048. D, GluRX:ChR2 mice also spent significantly less time performing self-grooming compared with Saline:ChR2 mice. *p = 0.036. E, No significant effect of light stimulation or group was detected on the time spent exploring their home cage. F, No significant effect of light stimulation or group was detected for freezing behavior in the presence of a juvenile intruder. G, Percentage of total time (3 min), showing social interaction, self-grooming, cage exploration, and freezing. Data are mean ± SEM.
