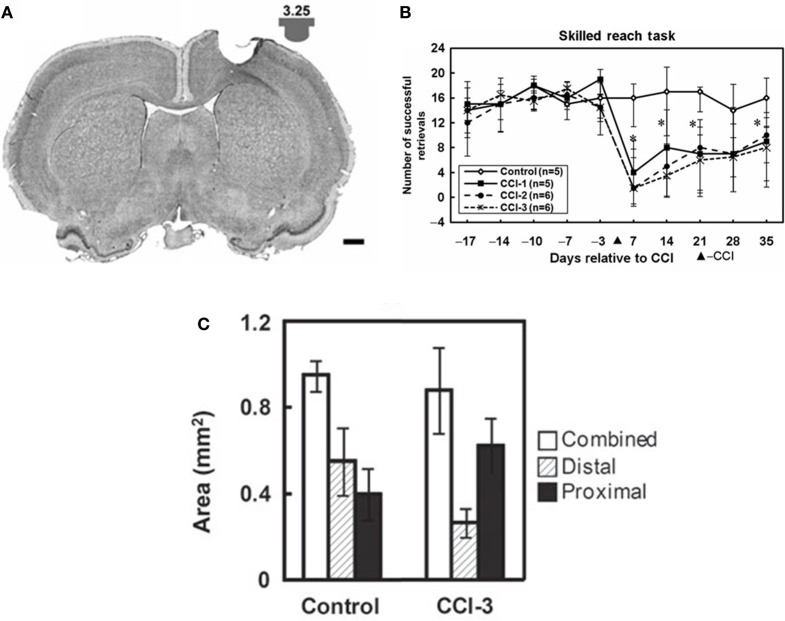
Figure 4.
Reorganization of the rat premotor cortex after controlled cortical impact in the primary motor cortex. (A) Coronal section through the primary motor cortex (caudal forelimb area, or CFA) of a rat approximately one month after a controlled cortical impact. Impactor tip dimension and shape is shown in the inset. (B) Behavioral performance on a single-pellet retrieval task before and after the injury (*p < 0.05). (C) Alteration in motor maps in the rat premotor cortex (rostral forelimb area, or RFA) approximately one month after a controlled cortical impact. In the premotor area that was spared by the lesion, digit representations contracted, while proximal representations expanded. This suggests that the behavioral recovery that was observed was due to compensatory kinematic patterns rather than true recovery (Nishibe et al., 2010).