Figure 5.
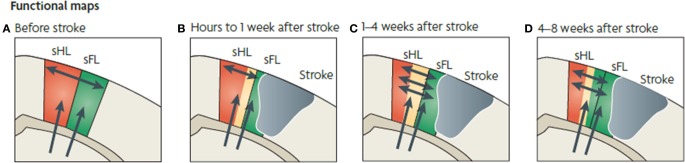
Functional map changes in forelimb (sFL) and hindlimb (sHL) somatosensory cortex after a focal infarct in mouse. Thalamic projections (arrows) and intracortical connections (double arrows) are also shown. (A) Normal somatosensory representation of sFL and sHL. (B) Within hours after focal infarct (gray), yellow areas show reduced sensory specificity, responding to both FL and HL stimulation. (C) Over the ensuing weeks, growth-promoting processes are triggered. Local axonal sprouting (double-headed arrows), dendritic spine expansion, and synaptogenesis occurs in the peri-infarct cortex. (D) Several weeks after stroke, specificity in sensory responses returns. Neurons that were formerly responsive to stimulation of hindlimb become responsive to forelimb stimulation (Murphy and Corbett, 2009).
