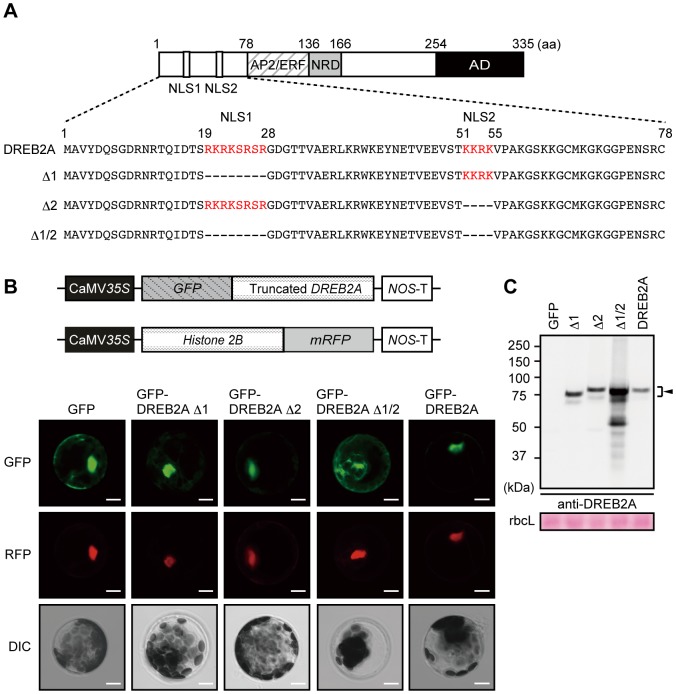
Figure 3. Nuclear localization of DREB2A is redundantly regulated by two nuclear localization signals (NLSs) and associated with a low DREB2A protein level.
(A) Schematic representation of the DREB2A protein showing the amino-terminal region, which contains two putative NLSs. The NLSs predicted by Liu et al. (1998) are shown in red. (B) Localization of GFP-DREB2A fusion proteins transiently expressed in Arabidopsis mesophyll protoplasts. A plasmid that constitutively expresses Histone 2B fused to mRFP was cotransfected into the protoplasts as a positive control for transfection and nuclear localization. Confocal images of the GFP field (GFP) and the RFP field (RFP) and differential interference contrast (DIC) images are shown from top to bottom. Bars = 20 µm. (C) Differences in the amounts of GFP-fused DREB2A proteins transiently expressed in Arabidopsis mesophyll protoplasts. Accumulation levels of the DREB2A proteins were determined by immunoblot analysis using the anti-DREB2A antibody. A plasmid that expresses the Luciferase reporter gene under the control of the CaMV 35S promoter was co-transfected as an internal control and the Luciferase activity was used for protein loading adjustment. The arrowhead indicates the major band of the GFP-fused DREB2A proteins. The Rubisco large subunit (rbcL) bands were visualized by Ponceau S and are shown as loading controls.