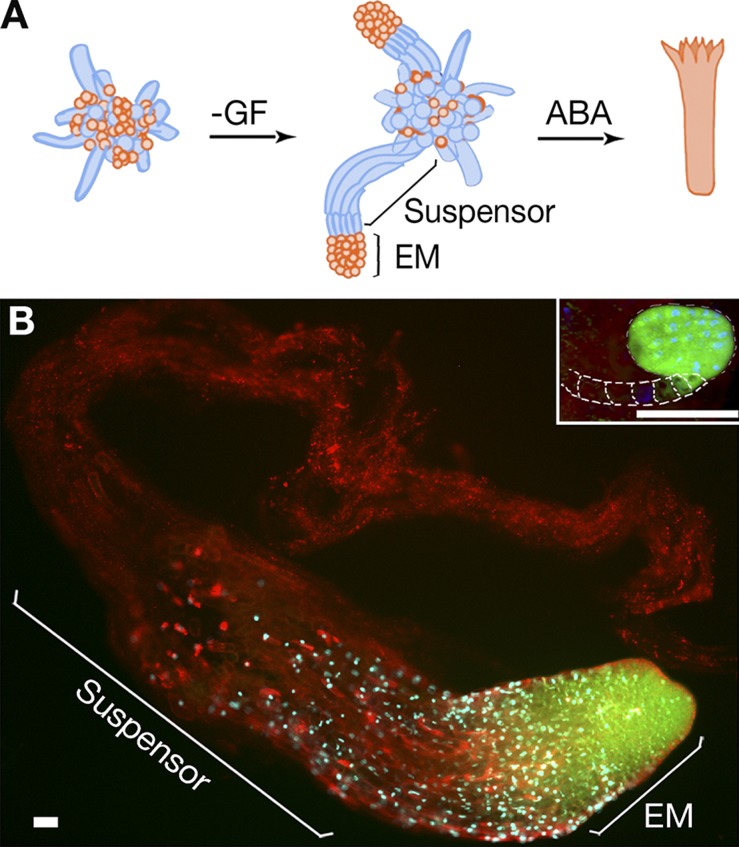
Figure 1.
Embryo development in P. abies. (A) A schematic model of somatic embryogenesis. Cell proliferation is stimulated by GF, auxin, and cytokinin. Early embryogenesis is induced by withdrawal of GF. An early embryo is composed of embryonal mass (EM) and a suspensor. Development to the cotyledonary stage is promoted by abscisic acid (ABA). Suspensors are eliminated before the cotyledonary stage. Dying or dead cells are colored in blue. (B) Embryos of P. abies and A. thaliana (inset; dashed lines indicate contour of suspensor) at the developmental stage before formation of cotyledons stained with fluorescein diacetate (FDA; green), DAPI (blue), and FM4-64 (red). The lack of FDA staining in the suspensor denotes the loss of cell viability. Note the giant size, as well as the higher suspensor-to-EM size ratio, for P. abies embryo as compared with the A. thaliana embryo. Bars, 50 µm.