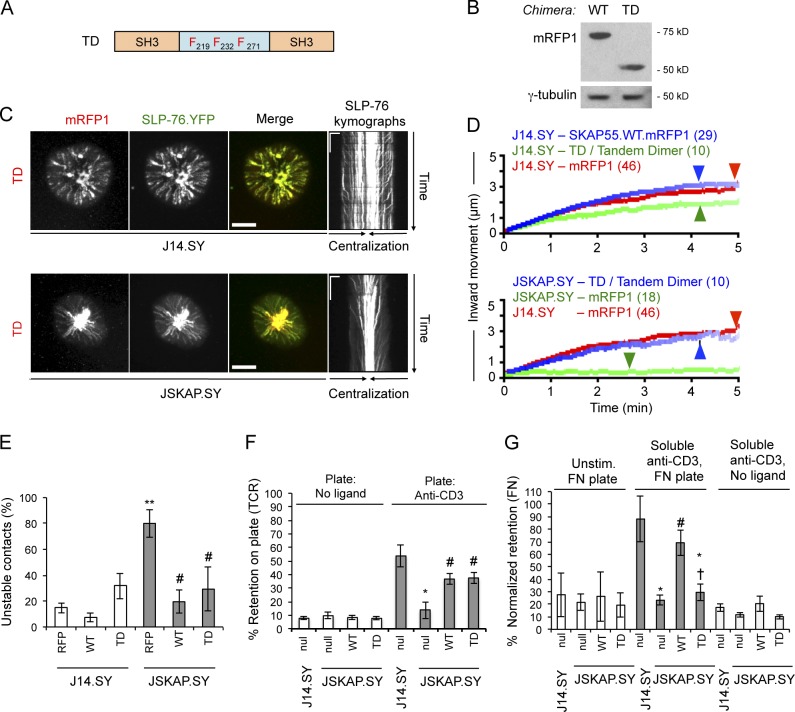
Figure 7.
An artificial SKAP55 TD is sufficient for recruitment to and stabilization of SLP-76 microclusters, and for adhesion to TCR but not integrin ligands. (A) Domain structure of the SKAP55 TD chimera. (B) J14.SY cells were transiently transfected with WT and TD chimeras and blotted to confirm comparable expression levels (n = 3). (C) J14.SY and JSKAP.SY cells expressing the TD chimera were stimulated, imaged, and presented as in Fig. 2 B. See Tables 1 and 2 for microcluster properties and experiment numbers. Bars: (conventional images) 10 µm; (kymographs) 5 µm × 60 s. (D) Composite microcluster traces for the conditions examined in C; numbers in parentheses indicate the total number of cells examined. Line intensity corresponds to the fraction of microclusters surviving; arrowheads identify points of half-maximal microcluster dissociation. (E) Fraction of cells scored as displaying unstable contacts (n = 6). (F and G) Fractional retention on anti-CD3–coated or fibronectin-coated coverslips, as described in Fig. 4 (n = 3). Error bars indicate mean ± SEM. From parental J14.SY cells (with or without mRFP1): *, P < 0.05; **, P < 0.01. From JSKAP.SY (with or without mRFP1): #, P < 0.05. From JSKAP.SY with SKAP55.WT.mRFP1 add-back: †, P < 0.05.