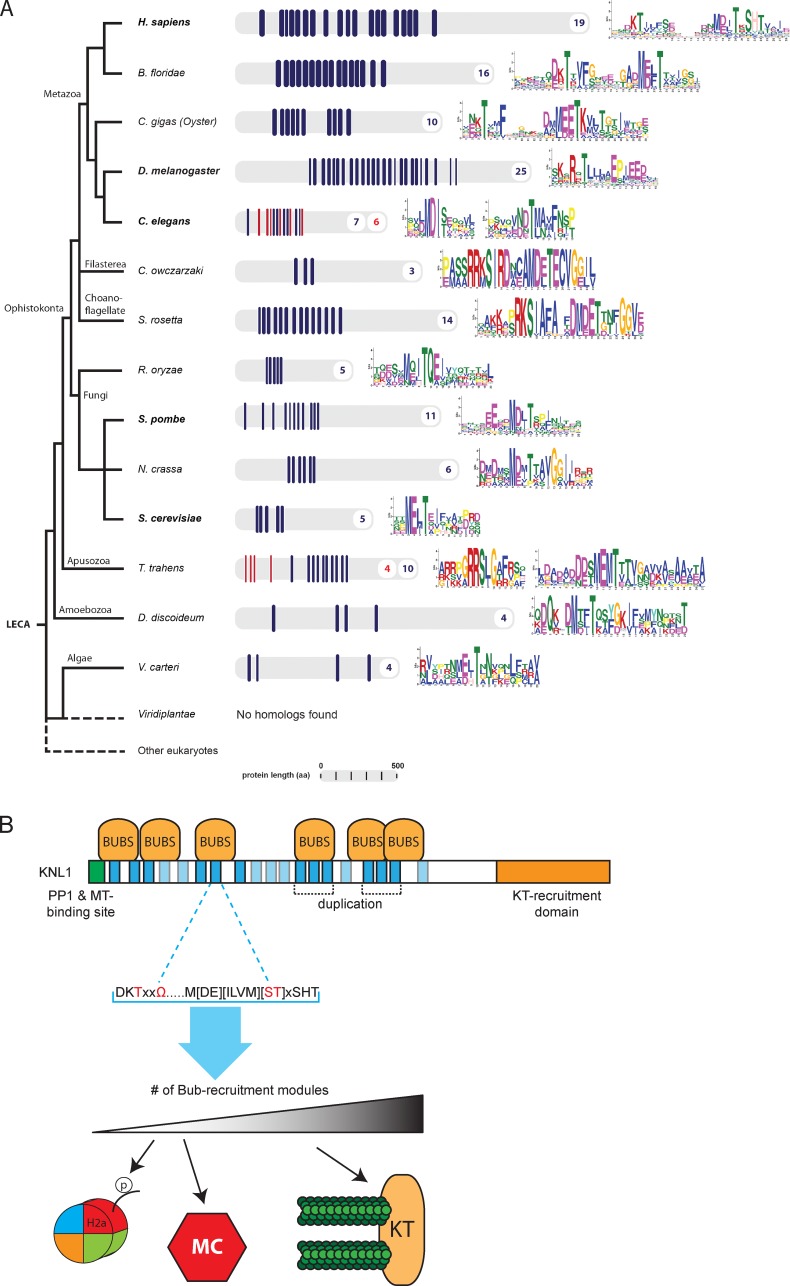
Figure 6.
TΩ-MELT module evolution and model. (A) Schematic representation of eukaryotic tree of life showing KNL1 homologues from indicated species. Repeating units are shown in blue and red with the number of repeats in corresponding colors. Repeat sequences are shown as sequence logos. (B) Model for TΩ-MELT function in human KNL1. Conserved (dark blue) and degenerated (light blue) TΩ-MELT modules (essential amino acids in red) in KNL1 can independently recruit BUB protein complexes (BUBs) to promote H2A-Thr120 phosphorylation and SAC activity (few modules, low BUB levels) and chromosome biorientation (increasing fidelity with increasing modules and BUB levels).