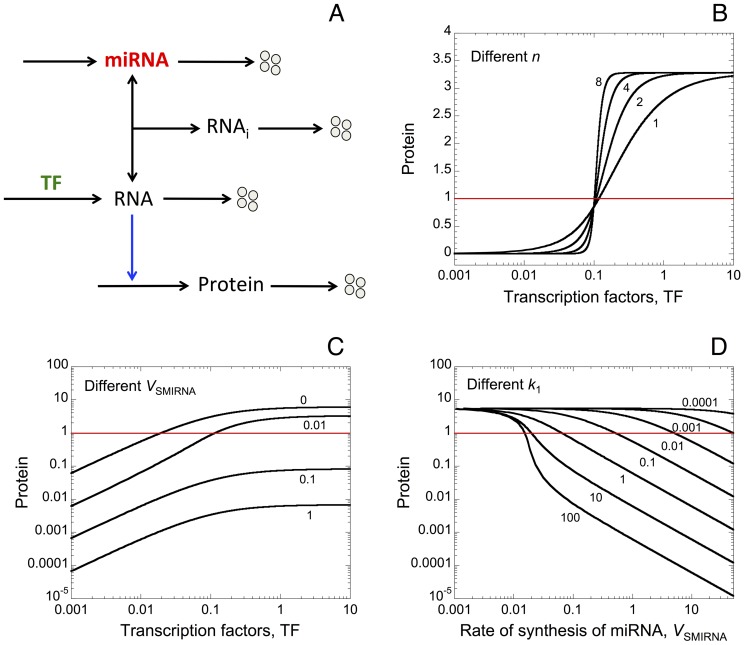
Figure 1. Oligomerization of transcription factors (TF) and miRNAs induce thresholds in protein expression.
(A) Minimal model for protein synthesis including a miRNA. TF activate, with or without oligomerization of TF, the synthesis of a messenger RNA (RNA). This RNA can form an inhibitory complex, RNAi, with a miRNA, which prevents it to encode the synthesis of the protein. We assume that the level of each component in the model can be controlled by synthesis and degradation. Steady-state levels of protein vs the level of TF are shown for different degrees of oligomerization of TF (n) in B, and for different rates of synthesis of miRNA (V SMIRNA) in C. Horizontal red lines indicate an arbitrary threshold of protein needed to promote a cellular response. (D) Steady-state levels of protein vs V SMIRNA for different rate constants of association between the RNA and the miRNA, k 1. Parameter values used in the simulations are as in Table 2.