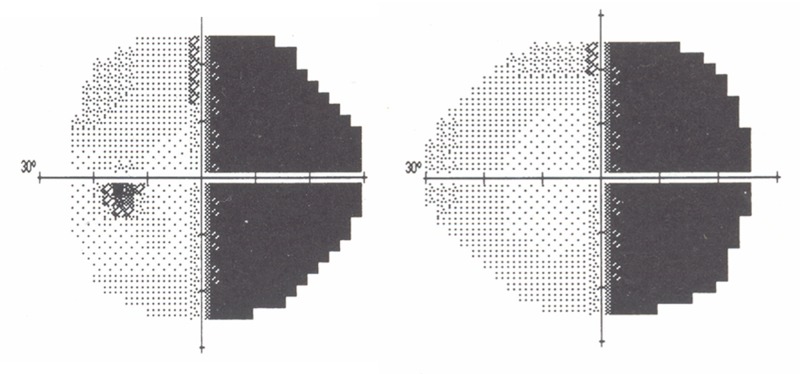
FIGURE 14.
Dense right hemianopic visual field defect in patient with left-sided Sturge-Weber syndrome. Patient with upper left facial port-wine stains and left occipital and parietal leptomeningeal enhancement noted on MRI (patient 18, Table 1). Much of the compensatory increase in deep cerebral venous drainage is routed posteriorly via the straight sinus toward the confluence of sinuses. The occipital lobe and visual cortex are more frequently overwhelmed by effects of transmitted venous hypertension with ensuing visual field defects (patients 1, 9, 10, 12, 15, 18 and 19, Table 1). Due to the increasing countercurrent drainage of the more posterior cerebral veins into the sagittal sinus (see Figure 19) increasing venous stasis, thrombosis with venous dysplasia is likely to be more common in veins subserving the posterior cortex.