Figure 8.
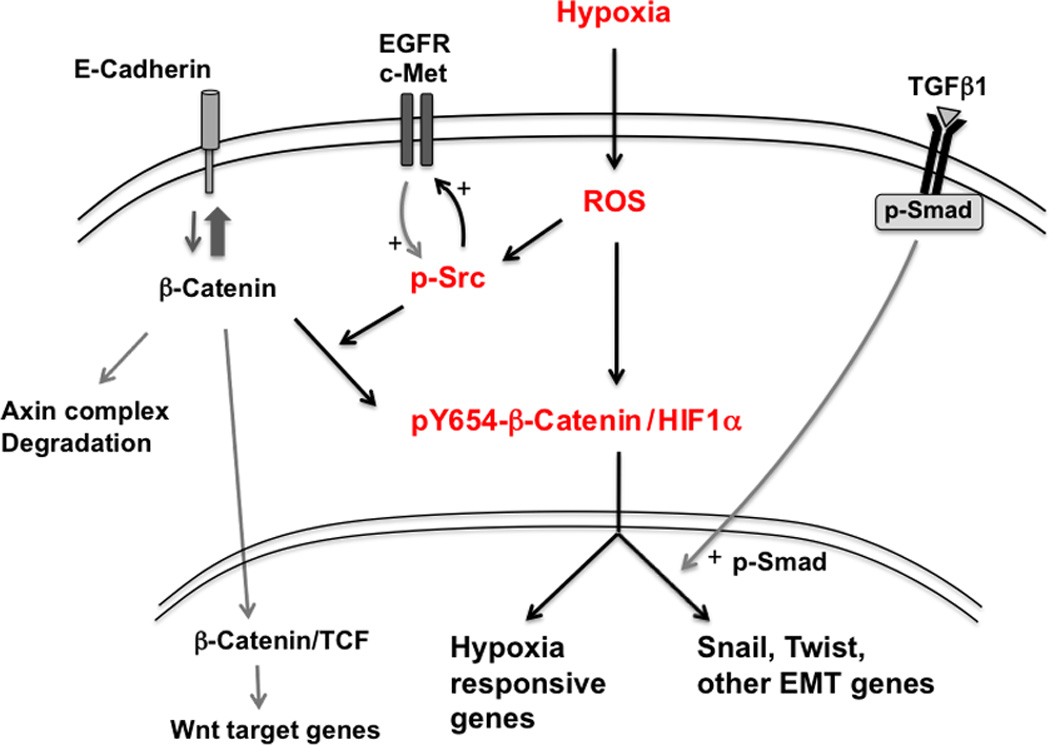
Schematic diagram illustrating central role for ROS and Src in hypoxia-induced pY654-β-catenin/HIF1α formation and tumor EMT. Hypoxia exposure generates reactive oxygen species (ROS) and stabilizes HIF1α (10). Increased ROS activity results in the activation of Src family kinase(s) (p-Src) (45) that then promotes activation of tyrosine kinases such as EGFR and c-Met, further promoting p-Src. Active Src phosphorylates β-catenin at Y654, favoring β-catenin association with HIF1α over β-catenin degradation, binding to E-cadherin, or association with TCFs in the Wnt pathway. pY654-β-catenin/HIF1α complexes promote transcription of EMT genes as well as other hypoxia responsive genes. Although not shown, Src is also in complexes of pY654-β-catenin/HIF1α. TGFβ1 signaling is not enhanced by hypoxia but remains active within the tumor microenvironment and further promotes hypoxia-induced EMT.
