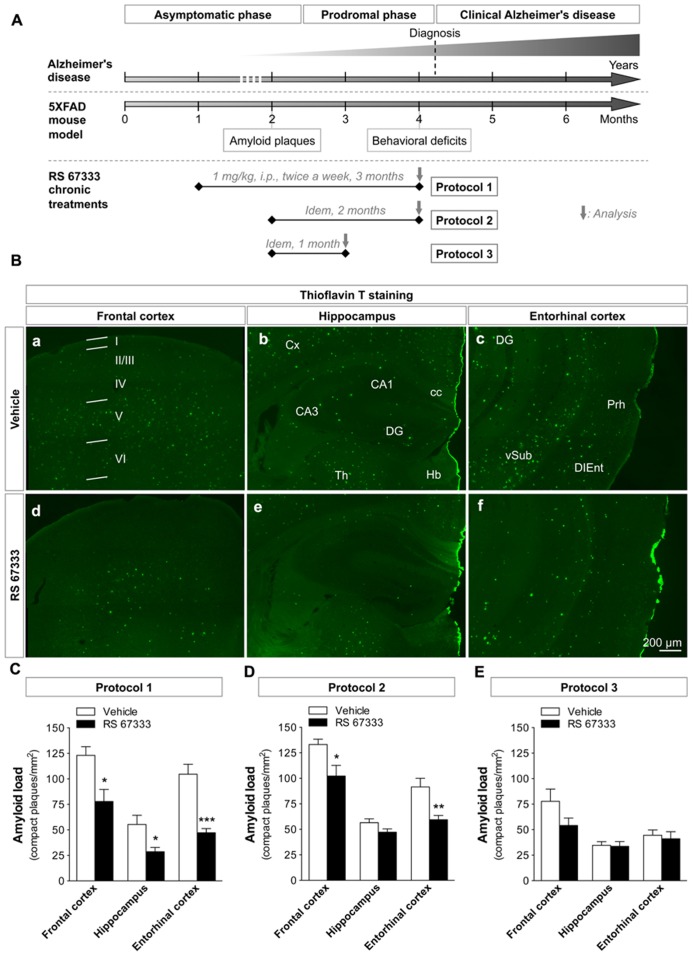
FIGURE 2.
Early, chronic administration of RS 67333 reduces the amyloid plaque load in 5XFAD mice. (A) Schematic model comparing the progression of AD in humans and of the AD-like pathology in 5XFAD mice. Aβ accumulation in 5XFAD mice starts at 2 months of age, which corresponds to AD asymptomatic phase in humans. The first memory and behavioral deficits in 5XFAD mice appear at about 4 months of age, which corresponds to the prodromal phase preceding the time of diagnosis in humans (clinical AD), prior to progressive accumulation of neuropathological alterations and memory deficits in 5XFAD mice. The time-course of the three different treatment protocols (protocols 1–3) with the 5-HT4 receptor agonist RS 67333 (1 mg/kg, i.p., twice a week) is shown below the schematic of disease progression. At the end of the treatment, the behavioral NOR test (only for mice treated according to protocol 2), Aβ40 and Aβ42 measurements in brain extracts, quantification of amyloid plaques and glial reactivity in brain slices were performed. (B) Representative images of thioflavin T staining of amyloid plaques in the frontal cortex (a,d), hippocampus (b,e), and entorhinal cortex (c,f) (B) from 5XFAD mice treated with RS 67333 (protocol 1) or vehicle alone. Images are mosaics collected with an AxioImager Z1 microscope, 10X objective (b–d). Quantification of Aβ load (number of plaques/mm2) in frontal cortex, hippocampus and entorhinal cortex following RS 67333 treatment using protocol 1 (C), protocol 2 (D) or protocol 3 (E). Data are the mean ± SEM, n ≤ 5/group. *p < 0.05, **p < 0.01, ***p < 0.001 compared with vehicle (unpaired Student’s t test). I-VI, cortical layers; Cx, cortex; cc; corpus callosum; CA1 and 3, cornu ammonis areas 1 and 3, DG; dentate gyrus; Th, thalamus; Hb, habenula; Prh, perirhinal cortex; DIEnt, dorsal intermediate entorhinal field; vSub, ventral subiculum.