Abstract
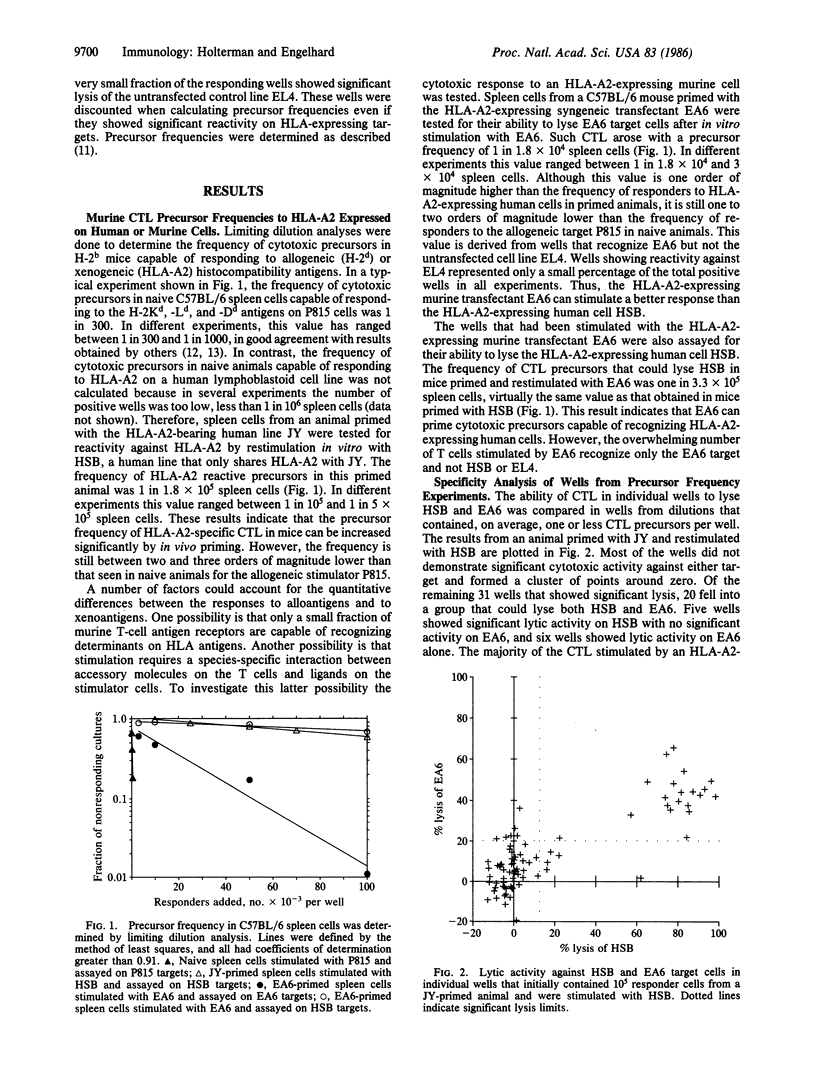
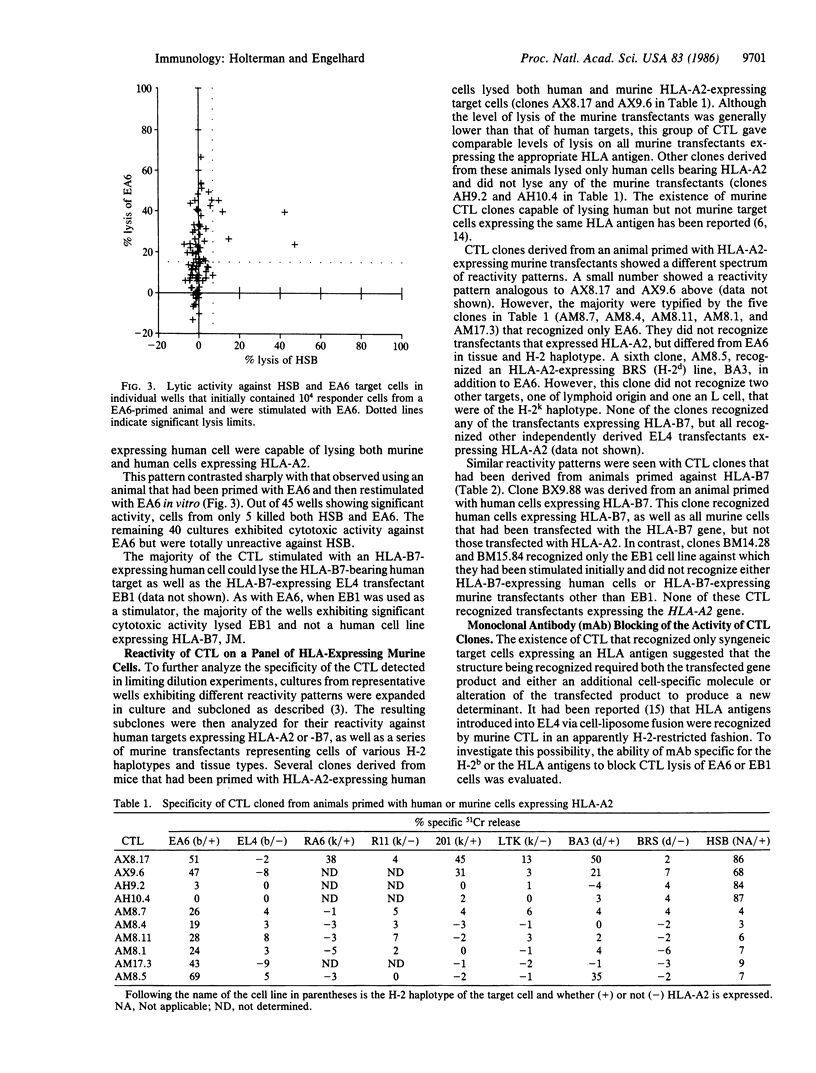
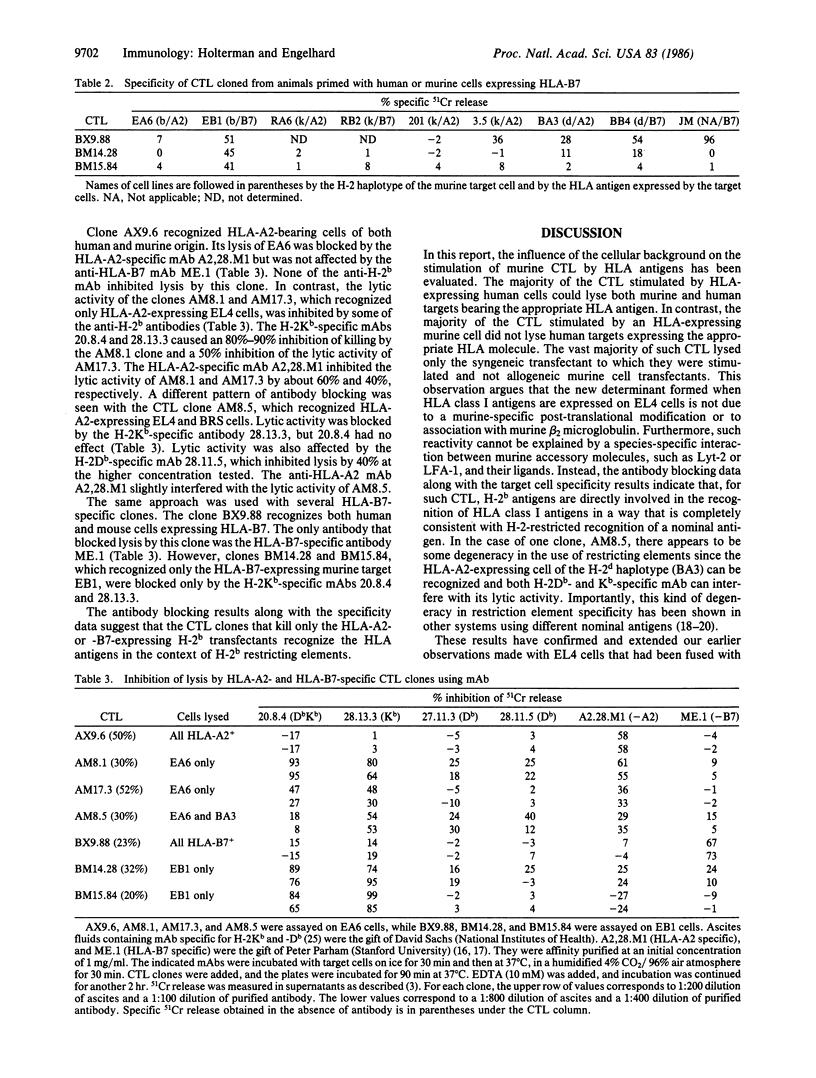
The frequency of murine cytotoxic T lymphocytes (CTL) capable of responding to HLA antigens expressed on human or murine cells was determined by limiting dilution analysis. HLA antigens expressed on human cells stimulated CTL with a precursor frequency of about 1 in 2 X 10(5) spleen cells in primed mice, over two orders of magnitude weaker than a primary allogeneic response. There was a 10-fold increase in the frequency of precursors responding to HLA antigens when they were expressed on murine cells. It was determined that the increased frequency of responders was due to CTL that could only recognize HLA antigens on the syngeneic murine line to which they had been stimulated and that these CTL could not lyse any other HLA expressing murine cells of different H-2 haplotypes. The lytic activity of these CTL was inhibited by H-2b-specific antibodies. These results indicate that such CTL recognize HLA antigens in the context of the H-2 major histocompatibility complex. The magnitude and specificity of CTL responses to xenoantigens are discussed in the context of a model for T-cell interactions with major histocompatibility antigens.
Full text
PDF

Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Achour A., Begue B., Gomard E., Paul P., Sayagh B., Van Pel A., Levy J. P. Specific lysis of murine cells expressing HLA molecules by allospecific human and murine H-2-restricted anti-HLA T killer lymphocytes. Eur J Immunol. 1986 Jun;16(6):597–604. doi: 10.1002/eji.1830160603. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Burakoff S. J., Engelhard V. H., Kaufman J., Strominger J. L. Induction of secondary cytotoxic T lymphocytes by liposomes containing HLA-DR antigens. Nature. 1980 Jan 31;283(5746):495–497. doi: 10.1038/283495a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ellis S. A., Taylor C., McMichael A. Recognition of HLA-B27 and related antigen by a monoclonal antibody. Hum Immunol. 1982 Aug;5(1):49–59. doi: 10.1016/0198-8859(82)90030-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Engelhard V. H., Benjamin C. Isolation and characterization of monoclonal mouse cytotoxic T lymphocytes with specificity for HLA-A,B or -DR alloantigens. J Immunol. 1982 Dec;129(6):2621–2629. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Engelhard V. H., Benjamin C. Xenogeneic cytotoxic T-cell clones recognize alloantigenic determinants on HLA-A2. Immunogenetics. 1983;18(5):461–473. doi: 10.1007/BF00364388. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Engelhard V. H., Powers G. A., Moore L. C., Holterman M. J., Correa-Freire M. C. Cytotoxic T lymphocyte recognition of HLA-A/B antigens introduced into EL4 cells by cell-liposome fusion. J Immunol. 1984 Jan;132(1):76–80. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Engelhard V. H., Strominger J. L., Mescher M., Burakoff S. Induction of secondary cytotoxic T lymphocytes by purified HLA-A and HLA-B antigens reconstituted into phospholipid vesicles. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1978 Nov;75(11):5688–5691. doi: 10.1073/pnas.75.11.5688. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goverman J., Hunkapiller T., Hood L. A speculative view of the multicomponent nature of T cell antigen recognition. Cell. 1986 May 23;45(4):475–484. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(86)90279-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grumet F. C., Fendly B. M., Fish L., Foung S., Engleman E. G. Monoclonal antibody (B27M2) subdividing HLA-B27. Hum Immunol. 1982 Aug;5(1):61–72. doi: 10.1016/0198-8859(82)90031-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hedrick S. M., Matis L. A., Hecht T. T., Samelson L. E., Longo D. L., Heber-Katz E., Schwartz R. H. The fine specificity of antigen and Ia determinant recognition by T cell hybridoma clones specific for pigeon cytochrome c. Cell. 1982 Aug;30(1):141–152. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(82)90020-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Herman A., Parham P., Weissman S. M., Engelhard V. H. Recognition by xenogeneic cytotoxic T lymphocytes of cells expressing HLA-A2 or HLA-B7 after DNA-mediated gene transfer. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1983 Aug;80(16):5056–5060. doi: 10.1073/pnas.80.16.5056. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hünig T. R., Bevan M. J. Antigen recognition by cloned cytotoxic T lymphocytes follows rules predicted by the altered-self hypothesis. J Exp Med. 1982 Jan 1;155(1):111–125. doi: 10.1084/jem.155.1.111. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Litzkas P., Jha K. K., Ozer H. L. Efficient transfer of cloned DNA into human diploid cells: protoplast fusion in suspension. Mol Cell Biol. 1984 Nov;4(11):2549–2552. doi: 10.1128/mcb.4.11.2549. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MacDonald H. R., Cerottini J. C., Ryser J. E., Maryanski J. L., Taswell C., Widmer M. B., Brunner K. T. Quantitation and cloning of cytolytic T lymphocytes and their precursors. Immunol Rev. 1980;51:93–123. doi: 10.1111/j.1600-065x.1980.tb00318.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maryanski J. L., Accolla R. S., Jordan B. H2-restricted recognition of cloned HLA class I gene products expressed in mouse cells. J Immunol. 1986 Jun 15;136(12):4340–4347. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Matis L. A., Longo D. L., Hedrick S. M., Hannum C., Margoliash E., Schwartz R. H. Clonal analysis of the major histocompatibility complex restriction and the fine specificity of antigen recognition in the T cell proliferative response to cytochrome C. J Immunol. 1983 Apr;130(4):1527–1535. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mulligan R. C., Berg P. Selection for animal cells that express the Escherichia coli gene coding for xanthine-guanine phosphoribosyltransferase. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1981 Apr;78(4):2072–2076. doi: 10.1073/pnas.78.4.2072. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Oi V. T., Morrison S. L., Herzenberg L. A., Berg P. Immunoglobulin gene expression in transformed lymphoid cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1983 Feb;80(3):825–829. doi: 10.1073/pnas.80.3.825. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ozato K., Sachs D. H. Monoclonal antibodies to mouse MHC antigens. III. Hybridoma antibodies reacting to antigens of the H-2b haplotype reveal genetic control of isotype expression. J Immunol. 1981 Jan;126(1):317–321. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ploegh H. L., Orr H. T., Strominger J. L. Major histocompatibility antigens: the human (HLA-A, -B, -C) and murine (H-2K, H-2D) class I molecules. Cell. 1981 May;24(2):287–299. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(81)90318-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Southern P. J., Berg P. Transformation of mammalian cells to antibiotic resistance with a bacterial gene under control of the SV40 early region promoter. J Mol Appl Genet. 1982;1(4):327–341. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Teh H. S., Harley E., Phillips R. A., Miller R. G. Quantitative studies on the precursors of cytotoxic lymphocytes. I. Characterization of a clonal assay and determination of the size of clones derived from single precursors. J Immunol. 1977 Mar;118(3):1049–1056. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yannelli J. R., Moore L. C., Engelhard V. H. Multiple epitopes on human and murine cells expressing HLA-B7 as defined by specific murine cytotoxic T cell clones. J Immunol. 1985 Aug;135(2):900–905. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


