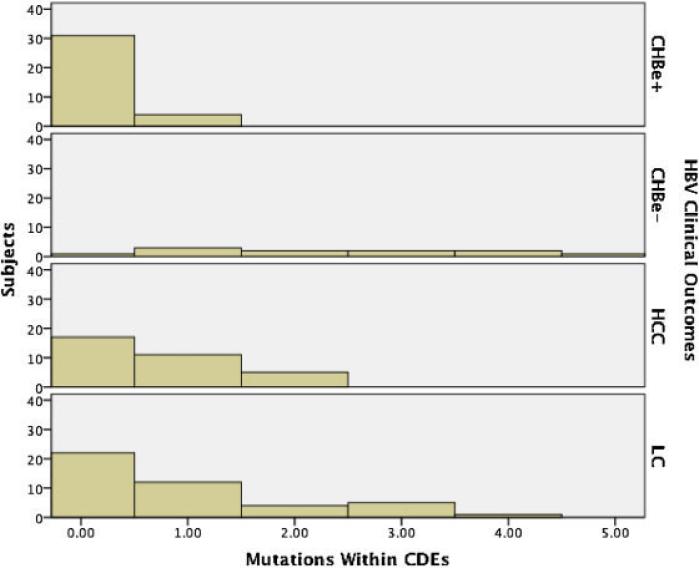
Fig. 1.
Mutations by HBV Disease state. The average number of non-synonymous mutations within cytotoxic T-lymphocyte directed epitopes (CDEs) were higher among progressive disease states. Individuals with chronic HBV infection and e antigen present (CHBe+) had fewer mutations than those with hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC) (P = 0.026), and liver cirrhosis (LC) (P = 0.007). Additionally, individuals with chronic HBV infection and e antigen present (CHBe+) had fewer mutations than individuals with chronic HBV and e antigen absent (CHBe–) (P = <0.003).